Copy link
Oculocardiac Reflex
Last updated: 01/20/2023
Key Points
- Oculocardiac reflex (OCR) is mediated by the trigeminal and vagus nerves.
- OCR usually presents as sinus bradycardia and is commonly seen during strabismus surgery with traction on the extraocular muscles.
- Cessation of the traction on the extraocular muscles usually terminates the reflex.
Introduction
- The oculocardiac reflex, also known as the Aschner reflex or trigeminovagal reflex, is defined by a 20% reduction in heart rate lasting 5 seconds or more from direct pressure on the globe or traction of the extraocular muscles, especially the medial rectus muscle.1,2
- OCR most commonly results in sinus bradycardia but can also lead to fatal arrhythmias, asystole, and even cardiac arrest.
- OCR is most commonly seen during strabismus surgery but can also be seen during sinus surgery, transsphenoidal surgery, following orbital trauma, or retrobulbar block.1
- OCR is a fatigable reflex with a decrease in intensity with repeated stimulation.1
Anatomy
- Afferent limb: Trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V); efferent limb: vagus nerve (cranial nerve X)
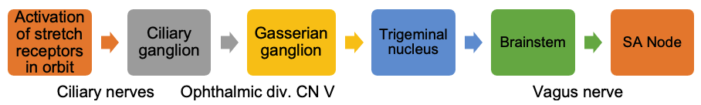
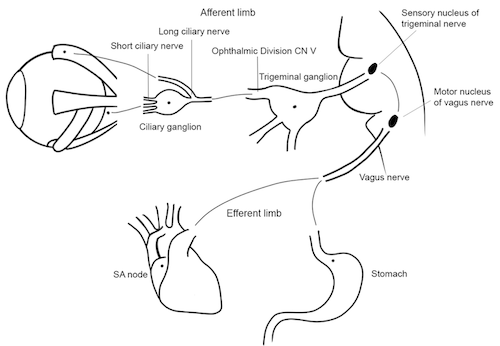
Figure 1. Oculocardiac reflex pathway. Illustration by Lindey Campagne, OD. Reproduced with permission from Michael Puente, MD. Link
Management
- Cessation of pressure on the globe or traction on the extraocular muscles usually terminates the reflex. The bradycardia typically resolves within a few seconds. If bradycardia persists, administer atropine (10-20 mcg/kg IV) or glycopyrrolate (10 mcg/kg IV).1,2
- Ensure adequate oxygenation, ventilation, and anesthetic depth
- Prophylactic administration of atropine or glycopyrrolate decreases the incidence of OCR. However, routine prophylactic administration of anticholinergics remains controversial.1
- While a retrobulbar block can decrease OCR by blunting the afferent limb of the reflex, it can trigger OCR from the pressure of the local anesthetic injection.1
Effect of Anesthetics
- Compared to volatile anesthetics, total intravenous anesthesia with propofol and remifentanil infusions increases the incidence of OCR.3 Among the volatile anesthetics, the incidence of OCR is highest with halothane, and no difference has been reported between sevoflurane and desflurane.3
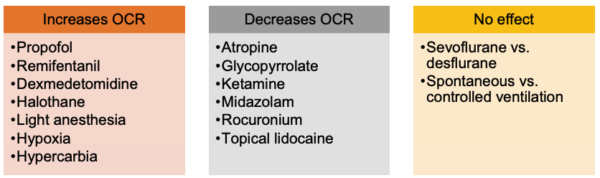
Adapted from Rodgers A, Cox RG. Can J Anaesth. 2010.
References
- Rodgers A, Cox RG. Anesthetic management for pediatric strabismus surgery: Continuing professional development. Can J Anaesth. 2010;57(6): 602-17. PubMed
- Dunville LM, Kamer J. Oculocardiac reflex. StatPearls. 2018. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2018. Link
- Choi SR, Park SW, Lee JH, et al. Effect of different anesthetic agents on oculocardiac reflex in pediatric strabismus surgery. J Anesth. 2009;23 (4): 489-93. PubMed
Other References
- Chatterjee D. Oculocardiac reflex. OpenAnesthesia. Published April 2017. Accessed January 25, 2023. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.