Copy link
Preoperative Laboratory Testing
Last updated: 10/16/2025
Key Points
- According to the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) practice advisory, baseline laboratory testing, such as blood counts, metabolic panel, and coagulation studies, should not be ordered routinely for patients without significant systemic disease (ASA I or II) undergoing low-risk procedures.1,2
- In higher-risk patients (ASA III or higher), selective preoperative testing may help identify modifiable risk factors and change perioperative management.
- In general, test results from within the last 6 months are sufficient, provided the patient’s medical history has not changed substantially.1
Indications for Preanesthesia Laboratory Testing
- For patients ASA Class III and higher (patients with severe systemic disease or greater complexity), preanesthesia testing should be ordered according to the patient’s individual risk factors as well as risks of the planned procedure (Table 1, Table 2).1,3
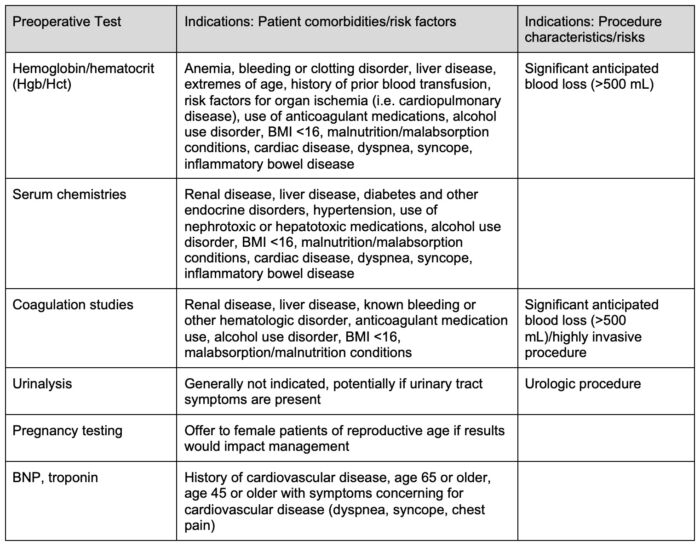
Table 1. Indications for preoperative laboratory testing.
Abbreviations: BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; BMI, body mass index
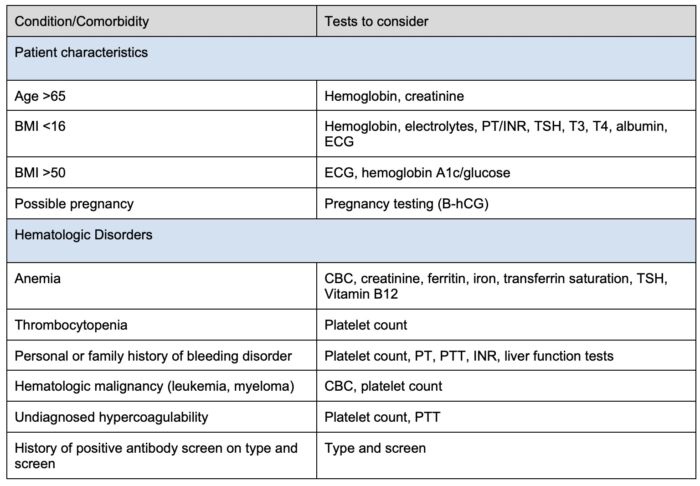
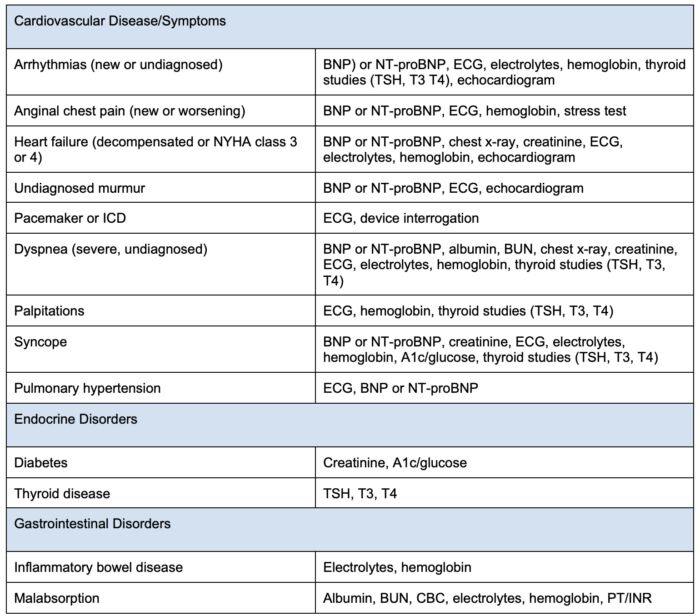
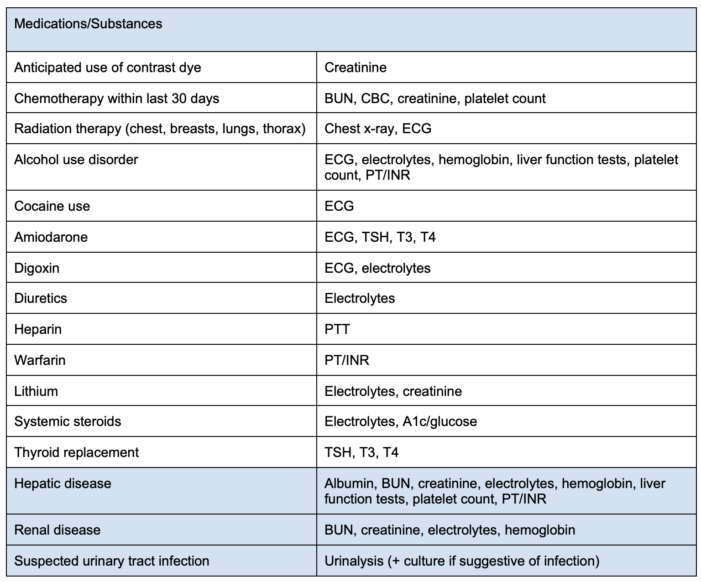
Table 2. Preoperative tests to consider based on patient comorbidities.
Abbreviations: BMI = body mass index, PT = prothrombin time, INR = international normalized ratio, TSH = thyroid stimulating hormone, T3 = triiodothyronine, T4 = thyroxine, ECG = electrocardiogram, B-hCG = betal human chorionic gonadotropin, CBC = completed blood cell count, PTT = partial thromboplastin time, BNP = brain natriuretic peptide, NT-proBNP = N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, BUN = blood urea nitrogen, ICD = internal cardioverter defibrillator. Adapted from Sweitzer B, Pfeifer K. Preoperative evaluation for noncardiac surgery in adults. In: UpToDate.4
Impacts of Preoperative Lab Testing
- Despite ASA guidelines and minimal impacts on clinical outcomes, the majority (51.6%) of low-risk patients receive laboratory testing before elective low-risk outpatient surgeries.5
- An estimated $373 million is spent annually in the United States on preoperative laboratory testing in low-risk (ASA I or II) patients undergoing elective outpatient surgery.5
- In low-risk (ASA I or II) patients, laboratory testing does not impact mortality and has a minimal impact on complication rates (2.5% without testing, 1.7% with testing).5
- Preoperative laboratory testing in low-risk patients has a high number needed to test to prevent both serious morbidity (599) and any complication (133).5
Preoperative Lab Testing and Perioperative Management
- Hemoglobin/Hematocrit
- Asymptomatic anemia in low-risk patients undergoing low-risk surgery is rare, and perioperative management is unlikely to change in patients with asymptomatic anemia.6
- Higher risk patients (ASA III or higher), especially those with renal disease, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, iron deficiency, and/or heart failure, have a much higher prevalence of anemia.3
- A thorough patient interview and medical record review should be conducted to identify risk factors, including prior blood transfusions, a history of coagulopathy (congenital or drug-induced), a history of thrombotic events, and other risk factors for organ ischemia. These risk factors should be used to determine the need for further laboratory testing.7
- In select patient populations (renal disease, anemia of chronic disease, transfusion refusal, etc.), preoperative erythropoietin administration with or without iron may reduce the need for transfusions.7
- Coagulation studies
- In patients with suspected coagulation disorders, risk factors (renal or liver disease, anticoagulant use, planned procedure with high risk of bleeding), or with excessive postoperative bleeding, the ASA recommends obtaining viscoelastic assays (thromboelastography, rotational thromboelastometry) and/or standard coagulation studies (international normalized ratio, activated partial thromboplastin time, fibrinogen).1,7
- Obtaining routine coagulation studies in asymptomatic, low-risk patients is unlikely to change management or impact outcomes.
- Abnormal coagulation studies may lead to changes in management, including discontinuation/adjustment of anticoagulant medication regiment or correction of coagulopathies (Vitamin K, prothrombin complex concentrate, fresh-frozen plasma).7
- Serum chemistries
- In patients with risk factors (ASA III or higher, renal disease, diabetes and other endocrine disorders, hypertension), measures of renal function (creatinine, blood urea nitrogen) may be used to guide fluid management and perioperative drug dosing.
- Electrolyte derangements identified through laboratory testing may help identify patients who require preoperative correction of such abnormalities to minimize risk for perioperative complications including arrhythmias.
- Particularly in patients with a history of diabetes, hyperglycemia on lab testing may identify patients who require closer blood glucose control to prevent infection and optimize postoperative wound healing.
- Cardiac biomarkers
- The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association recommend preoperative measurement of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) (and consider measurement of troponin) in patients with known cardiovascular disease, patients age 65 or older, and patients age 45 or older with symptoms suggestive of cardiovascular disease.3
- BNP/NT-proBNP and troponin have both high prognostic value and excellent negative predictive value for perioperative cardiac complications.3
- Despite the value of cardiac biomarker testing in risk stratification, no studies have established clear perioperative management guidelines to improve outcomes in patients with elevated preoperative cardiac biomarkers.3
- Urinalysis
- Preoperative urinalysis is only indicated for specific planned procedures (urologic procedure, prosthesis implantation) or for patients with urinary tract symptoms.1
- Abnormal urinalysis findings in symptomatic patients or those undergoing urologic procedures may lead to delaying elective surgery or initiation of antimicrobial therapy.
- In patients undergoing nonurologic surgery, screening and treating patients for asymptomatic bacteriuria has not been shown to improve outcomes or reduce complications.8
- Pregnancy testing
- While preoperative pregnancy testing is not indicated routinely, the ASA states that pregnancy testing should be offered to female patients of childbearing age with unknown pregnancy status if knowledge of pregnancy would change management (delay of elective surgery, changes to anesthetic or surgical plan).1
References
- ASA Committee on Standards and Practice Parameters. Practice advisory for preanesthesia evaluation: An updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists task force on preanesthesia evaluation. Anesthesiology. 2012;116(3):522. PubMed
- American Society of Anesthesiologists. American Society of Anesthesiologists releases list of commonly used tests and treatments to question-AS PART OF CHOOSING WISELY® CAMPAIGN. American Society of Anesthesiologists. Published October 12, 2013. Accessed October 16, 2025. Link
- Thompson A, Fleischmann KE, Smilowitz NR, et al. 2024 AHA/ACC/ACS/ASNC/HRS/SCA/SCCT/SCMR/SVM guideline for perioperative cardiovascular management for noncardiac surgery: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2024;150(19):e351-e442. PubMed
- Sweitzer B, Pfeifer K. Preoperative evaluation for noncardiac surgery in adults. UpToDate. Updated: May 27, 2025. Accessed September 20, 2025. Link
- Taylor GA, Oresanya LB, Kling SM, et al. Rethinking the routine: Preoperative laboratory testing among American Society of Anesthesiologists class 1 and 2 patients before low-risk ambulatory surgery in the 2017 National Surgical Quality Improvement Program cohort. Surgery. 2022;171(2):267-274. PubMed
- Olson RP, Stone A, Lubarsky D. The prevalence and significance of low preoperative hemoglobin in ASA 1 or 2 outpatient surgery candidates. Anesth Analg. 2005;101(5):1337-1340. PubMed
- Practice Guidelines for Perioperative Blood Management: An updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on perioperative blood management*. Anesthesiology. 2015;122(2):241. PubMed
- Salazar JG, O’Brien W, Strymish JM, et al. Screening and treatment for preoperative asymptomatic bacteriuria with postoperative outcomes among US veterans. JAMA Surg. 2019;154(3): 241-8. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.