Copy link
Preoperative Cardiac Risk Stratification and Evaluation
Last updated: 10/16/2025
Key Points
- Preoperative cardiac risk stratification remains the cornerstone of preoperative risk assessment before proceeding with noncardiac surgery.
- In 2024, the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA) updated their guidelines to include risk assessment tools, along with risk modifiers, which enable the consideration of additional comorbid conditions, such as frailty.
- A preoperative multidisciplinary approach is the key to further evaluating the overall risk, rather than relying on a single test or evaluation parameter.
Introduction and Pathophysiology
Epidemiology
- Cardiovascular risk factors are reported in about 45% of surgical patients who are older than 45 years. This prevalence is increasing over time, with the expectation that atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease will be diagnosed in nearly 25% of surgical patients.1
- In adults older than 45 years undergoing in-hospital surgery, perioperative death, myocardial infarction, or ischemic stroke occurred in 1 of every 33 admissions. A total of more than 150,000 annual perioperative events in the United States.2
- Patients undergoing vascular, thoracic, and solid organ transplantation had the highest rates of perioperative cardiovascular events.
- Perioperative cardiovascular complications are associated with increased length of hospital stay, higher morbidity, higher cost, and increased mortality.1,3
- Preoperative evaluation and risk stratification of patients with cardiovascular disease risk or cardiovascular comorbid conditions undergoing noncardiac surgery is crucial, as these patients are at an increased risk for major adverse cardiac events.
- A multidisciplinary approach is increasingly utilized to manage complex conditions and incorporate a perioperative medicine clinical pathway for high-risk patients.
- Preoperative risk assessment, cardiac testing, and further optimization plans are to be discussed among the anesthesiologist, cardiologist, and surgeons to ensure a safe perioperative care plan is in place and achieve a shared decision-making based on each patient’s risk-benefit profile.
- In this summary, we will focus on addressing methods of risk stratification, the role and indications of preoperative cardiac testing, and a stepwise approach to preoperative cardiac risk assessment and testing in preparation for noncardiac surgery.
Preoperative Risk Stratification and Cardiac Diagnostic Tests
Cardiovascular Risk Indices
- To evaluate the likelihood of perioperative cardiac adverse events, several risk stratification indices have been developed and validated using large observational data.
- Risk indices can be used in addition to surgery-related and patient-related risk factors.
- The 2024 AHA/ACC guidelines gave a class 2a recommendation to use a validated risk prediction tool in patients with known cardiovascular disease undergoing noncardiac surgery as a valuable tool to estimate the risk of perioperative Major Adverse Cardiac Events (MACE).1
- One of the commonly used risk assessment tools is the Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI). Tables 1 and 2 summarize the criteria and the calculated risk based on RCRI.
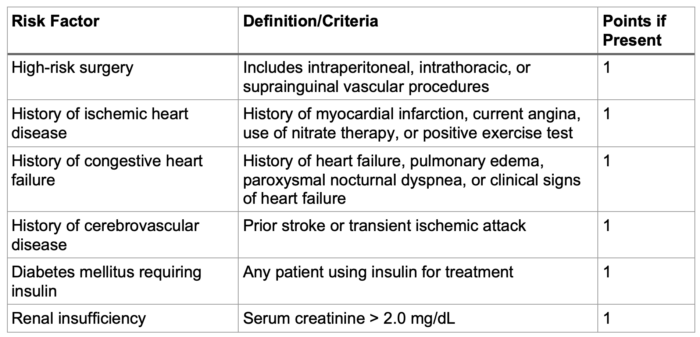
Table 1. Criteria for revised cardiac risk index
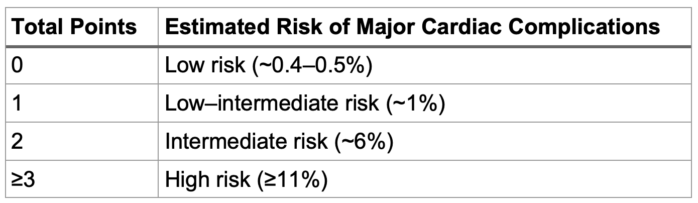
Table 2. Calculated risk of major adverse cardiac events based on the RCRI score
- The National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) /American College of Surgeons (ACS) risk assessment index includes the type of surgery, as well as the patient’s functional status and any additional cardiac and noncardiac comorbid conditions. Link In addition to evaluating the risk of major adverse cardiac events, NSQIP ACS provides an estimated risk for various outcomes, including complications, admission to a skilled nursing facility, and the expected length of hospital stay.4 The threshold for an elevated risk of MACE is greater than 1%.
Functional Capacity Assessment
- A class 2a recommendation from the 2024 AHA/ACC guidelines is to evaluate the patient’s functional capacity using a structured tool, such as the Duke Activity Status Index (DASI), which is reasonable for stratifying a patient’s risk for MACE.
- Functional capacity is an important predictor of the risk of adverse cardiovascular events after noncardiac surgery.
- Functional capacity assessment can identify patients who may require additional cardiac testing before undergoing noncardiac surgery.
- This can be achieved by asking if the patient can climb two flights of stairs (equivalent to more than 4 metabolic equivalents or METs) or by calculating the patient’s DASI score. DASI scores of ≤ 34 were associated with increased odds of 30-day death or myocardial ischemia.5
- An exercise stress test can provide an objective measurement of the patient’s functional capacity.
Frailty
- Frailty is a multidimensional syndrome that results from physiological decline and increased vulnerability to stress. It is an independent risk factor for adverse outcomes after noncardiac surgery, including cardiac complications, infections, increased risk of falls, functional decline, morbidity, and mortality.
- The prevalence of frailty in patients aged 65 years and older is 10% and more than 25% in patients who are aged 85 years and older. Older women are twice as likely to have frailty as men.
- It is a class 2a recommendation to perform a preoperative frailty assessment using a validated tool in all patients who are 65 years and older or those 64 years and younger with perceived frailty to evaluate their perioperative risk and guide further optimization and shared decision-making.1
- Validated frailty assessment tools include Physical Frail Phenotype (Fried Phenotype) (Score 0-5), Edmonton Frail Scale (10 items), and Clinical Frailty Scale (9 categories from fit to terminally ill).
Biomarkers
- In patients with known cardiovascular disease or those 65 years and older or those 45 years and older with symptoms suggestive of cardiovascular disease undergoing elevated risk noncardiac surgery, it is reasonable to measure the B-type natriuretic peptide or the N-terminal Pro-B-type natriuretic peptide before surgery to supplement the evaluation of perioperative cardiac risk.1
- In patients with known cardiovascular disease, 65 years and older, or 45 years and older with symptoms suggestive of cardiovascular disease, undergoing elevated risk noncardiac surgery, it is a class 2b (might be reasonable) to measure cardiac troponin before surgery to supplement the evaluation of preoperative cardiac risk.1
- Both biomarkers can quantify myocardial injury and cardiac wall stress, both with prognostic value and excellent negative predictive value for perioperative cardiac complications.
- There is no current evidence to suggest that patients with elevated preoperative biomarkers should undergo further management that would improve perioperative cardiovascular outcomes.
- Biomarkers in low-risk patients have not been evaluated.
Preoperative Cardiac Diagnostic Tests (Recommendations from the AHA/ACC Guidelines)
12-Lead Electrocardiogram Indications
- For patients with coexisting cardiovascular disease undergoing elevated-risk surgery, a preoperative resting 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is reasonable to establish a preoperative baseline and guide perioperative management.
- For patients undergoing noncardiac surgery with new ECG changes, further evaluation is reasonable to refine the assessment of the cardiovascular risk.
- Asymptomatic patients undergoing elevated-risk surgery without coexisting cardiovascular disease, a preoperative 12-lead ECG may be considered to establish a baseline.
- For asymptomatic patients undergoing low-risk surgery, a routine preoperative 12-lead ECG is not recommended.
Evaluation of Left Ventricular (LV) Function
- In patients with new dyspnea undergoing noncardiac surgery, physical examination findings of heart failure, or suspected new/worsening ventricular dysfunction, it is recommended to perform preoperative evaluation of LV function to help guide perioperative management (Class 1 recommendation).
- In patients with a known diagnosis of heart failure with worsening dyspnea or other change in clinical status undergoing noncardiac surgery, preoperative assessment of LV function is reasonable to help guide perioperative management.
- Routine preoperative evaluation of the LV function is not recommended in asymptomatic stable patients undergoing noncardiac surgery.
Evaluation of Right Ventricular (RV) Function
- Patients with mitral regurgitation, tricuspid regurgitation, or pulmonary hypertension can have RV dysfunction.
- Echocardiography is the first diagnostic test to assess RV function
- Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging is the gold standard for quantitative assessment of the RV volume and function, and may be the appropriate test for a selected group of patients.
Stress Testing
- For patients undergoing elevated-risk noncardiac surgery with poor or unknown functional capacity and elevated risk for perioperative cardiovascular events based on a validated risk tool, stress testing may be considered to evaluate for inducible myocardial ischemia.
- In patients who are at low risk for perioperative cardiovascular events, have adequate functional capacity with stable symptoms, or are undergoing low-risk procedures, routine stress testing before noncardiac surgery is not recommended.
A Stepwise Approach to Perioperative Cardiac Assessment
The 2024 AHA/ACC Guidelines for Perioperative Cardiovascular Management of Noncardiac Surgery propose a framework for perioperative cardiac risk stratification and management, focusing on best practices and recommendations.
The stepwise approach highlights the following (see figures 1-3).
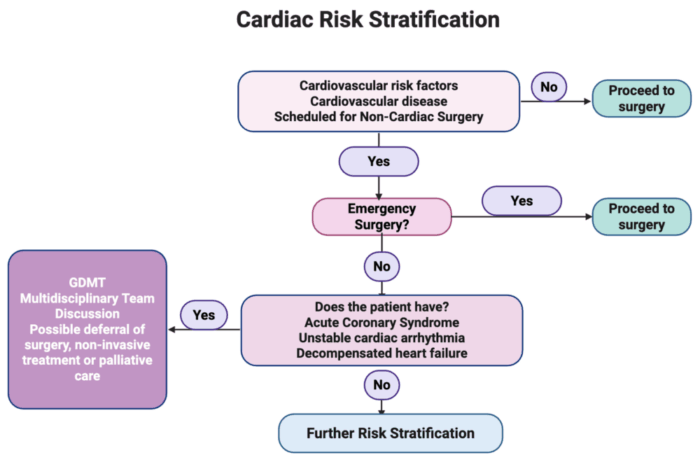
Figure 1. Cardiac risk stratification. Assessment of acute cardiac conditions. Abbreviation: GDMT, Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy. Created in BioRender. Mohamed, B. (2025) Link
- Patients with no risk factors for cardiovascular disease and no coexisting cardiovascular disease can proceed with surgery without further cardiac testing.
- Those with risk factors or coexisting cardiovascular disease and undergoing emergency surgery will have to proceed with surgery.
- Those with risk factors and coexisting cardiovascular disease undergoing elective noncardiac surgery with any of the following acute cardiac conditions should be referred for further cardiac evaluation and management, including guideline-directed management and therapy. A multidisciplinary discussion is needed for deferral of surgery, offering noninvasive management or palliative care.
- Acute coronary syndrome
- Unstable cardiac arrhythmia
- Decompensated heart failure
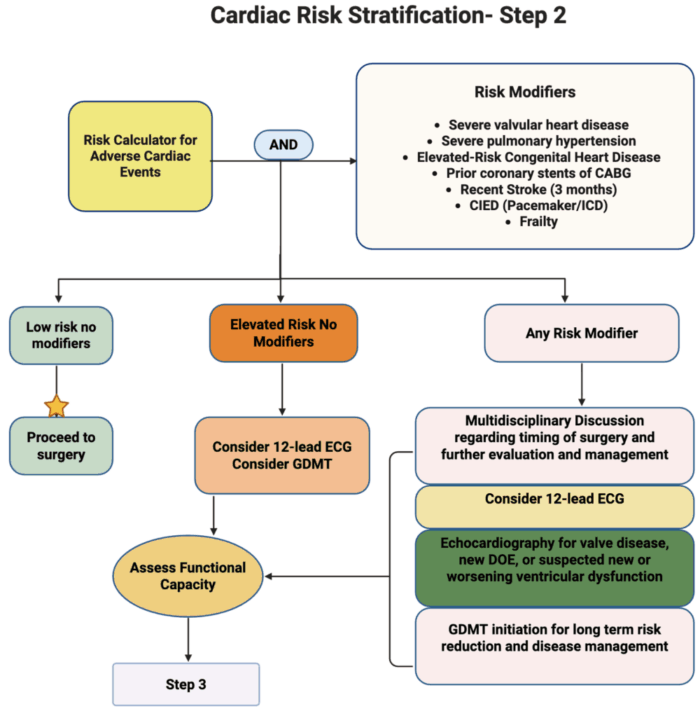
Figure 2. Risk Stratification of Cardiovascular Disease for elevated risk and patients with risk modifiers. Created in BioRender. Mohamed, B. (2025) Link
- Patients without acute cardiac conditions will be assessed using any of the validated risk assessment tools (RCRI or NSQIP). More than 1% risk of MACE is considered an elevated risk.
- Patients will also be evaluated for any of the following comorbid cardiac conditions, known as risk modifiers:
- Severe valvular heart disease
- Severe pulmonary hypertension
- Elevated risk congenital heart disease
- Prior coronary stent and or coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- Recent stroke (within 3 months)
- Cardiac Implantable electronic device (pacemaker or defibrillator)
- Frailty
- Patients with low calculated risk and no risk modifiers will proceed with surgery.
- Patients with an elevated calculated risk (more than 1%) and no risk modifiers should be evaluated for
- Potential role of 12-lead ECG (class 2b)
- Consider initiation of guideline-directed management and therapy for cardiovascular risk reduction and disease management.
- Patients with ANY of the risk modifiers (low or elevated risk)
- Multidisciplinary discussion regarding
- Timing of surgery
- Further perioperative cardiac testing and management.
- 12-lead ECG in patients with symptomatic cardiovascular disease (class 2a)
- Echocardiography for the following indications:
- Moderate or severe valvular stenosis or regurgitation (class 1 recommendation)
- New onset dyspnea (class 1 recommendation)
- Suspected new ventricular dysfunction.
- Suspected worsening ventricular dysfunction.
- Consider initiation of guideline-directed management and therapy for long-term cardiovascular risk reduction and disease management.
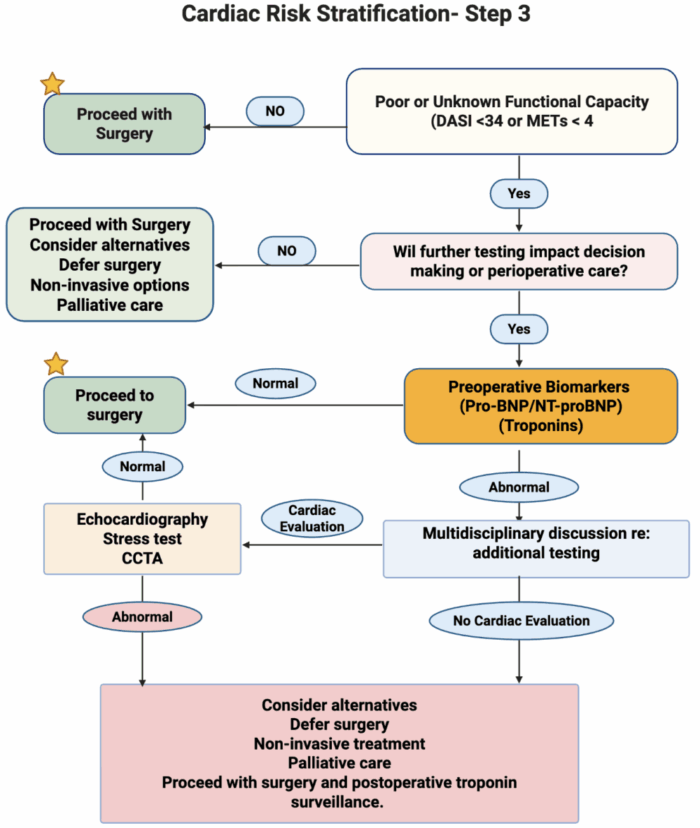
Figure 3. Further evaluation and risk stratification based on functional capacity. Created in BioRender. Mohamed, B. (2025) Link
- Any patient with elevated risk or any of the risk modifiers should have an assessment of their functional capacity (poor functional capacity defined as METs < 4 or DASI score < 34)
- Those without a poor or unknown functional status can proceed with surgery
- Those with poor or unknown functional status can be evaluated if further testing will change decision-making or perioperative care
- If further testing will change the decision-making or perioperative care→, proceed with biomarker testing.
- Biomarkers assessment
- If normal → proceed with surgery
- If abnormal → multidisciplinary discussion to
- Proceed with further cardiac testing or
- Proceed with surgery or
- Deferring surgery and proceeding with less invasive alternatives or palliative care.
- Cardiac evaluation (if normal, proceed with surgery)
- Stress test
- Coronary computed tomography angiogram
- Consider echocardiography
- Abnormal cardiac testing
- Multidisciplinary discussion to evaluate risk versus benefits
- Defer surgery and proceed with less invasive alternatives or palliative care
- Proceed with surgery and consider postoperative troponin surveillance.
References
- Thompson A, Fleischmann KE, Smilowitz NR, et al. 2024 AHA/ACC/ACS/ASNC/HRS/SCA/SCCT/SCMR/SVM guidelines for perioperative cardiovascular management for noncardiac surgery: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2024;150(19):e351-e442. PubMed
- Smilowitz NR, Gupta N, Ramakrishna H, et al. Perioperative major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events associated with noncardiac surgery. JAMA Cardiology. 2017;2(2):181-187. PubMed
- Devereaux PJ, Sessler DI. Cardiac complications in patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery. New England Journal of Medicine. 2015;373(23):2258-2269. PubMed
- American College of Surgeons/National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. ACS Surgical Risk Calculator. Updated April 2025. Accessed October 1, 2025. Link
- Wijeysundera DN, Beattie WS, Hillis GS, et al. Integration of the Duke Activity Status Index into preoperative risk evaluation: a multicentre prospective cohort study. British Journal of Anaesthesia. 2020;124(3):261-270. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.