Copy link
Pheochromocytoma
Last updated: 02/19/2025
Key Points
- Chronic elevations in circulating catecholamines can result in several end-organ manifestations, including acute and chronic cardiomyopathy.
- Preparation for pheochromocytoma surgery takes 10-14 days to control hypertension, tachycardia, and restoration of intravascular volume.
- The critical portions of a pheochromocytoma excision surgery are intubation, insufflation of the abdomen (during laparoscopic cases), tumor manipulation, and adrenal vein clamping.
- Short-acting vasopressors and antihypertensives should be used for hemodynamic management, and medications with sympathomimetic properties that may cause histamine release or have dopaminergic activity should be avoided.
Introduction
- The incidence of pheochromocytoma in the general population is about 1 per 100,000 person-year. It occurs most often in patients between 40-60 years of age.1 The estimated incidence of pheochromocytoma in hypertensive adults is about 0.2-0.6%.2
- Around 40% of all cases are associated with a genetic condition. These patients tend to be younger and are more likely to have bilateral tumors. The genetic conditions include1,3
- Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
- Neurofibromatosis type 1
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A and 2B
- Paraganglioma syndrome 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
- Sturge-Weber syndrome
- While pheochromocytomas most commonly present as sporadic unilateral adrenal mass, other special clinical scenarios may be best remembered by the so-called “Rule of 10s.”4 Approximately 10% of pheochromocytomas can be:
- metastatic
- extra-adrenal (paragangliomas)
- bilateral
- malignant
- found in children
- not associated with hypertension
Pathophysiology
- Pheochromocytomas are catecholamine-secreting tumors of the adrenal gland derived from chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla. They are now recognized as part of a family of neuroendocrine tumors derived from embryologic neural crest cells called paragangliomas. Extra-adrenal sympathetic paragangliomas are usually functional and produce catecholamines. The perioperative management of both pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma are nearly identical.1
- The perioperative management of pheochromocytoma requires close collaboration between the anesthesia team, surgeon, endocrinologist, and postoperative team. Perioperative morbidity and mortality of unrecognized pheochromocytoma is extremely high. About 25-50% of hospital deaths for patients with pheochromocytoma occur during induction of anesthesia or unrelated surgery.1 Mortality can be as high as 80% if an unanticipated pheochromocytoma crisis is precipitated.5
Metabolic and Circulatory Manifestations
- Diabetes is a common metabolic derangement, occurring in about 36% of all patients with pheochromocytoma, which is due to catecholamine-induced insulin suppression.6
- Chronic elevation in serum catecholamines can result in cardiac and vascular manifestations. Excessive catecholamine may cause acute stress-induced cardiomyopathy (“Takotsubo”) or chronic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.7 End-organ dysfunction from circulating catecholamines can manifest in the following ways:8
- Brain: Stroke, encephalopathy
- Ocular: Acute blindness, retinopathy
- Heart: Cardiomyopathies, arrhythmias, myocarditis, angina, myocardial infarction
- Vascular: Orthostatic hypotension, shock, aortic dissection, ischemia
- Lungs: Pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension
- Gastrointestinal: Intestinal ischemia
- Kidneys: Acute renal failure, hematuria
Diagnosis
- The classic triad of symptoms for pheochromocytoma is episodic headaches, sweating, and tachycardia.1 Other symptoms include difficult-to-control hypertension, hypertension that occurs at a young age, orthostatic hypotension, palpitations, anxiety, weakness/fatigue, flushing, pallor, nausea/vomiting, dizziness/vertigo, chest pain, abdominal pain, flank pain, dyspnea, constipation, paresthesia, and tremor.
- The combination of paroxysmal headache, sweating, and hypertension is more sensitive than any single blood test.
- Clinical suspicion based on symptoms or familial history will necessitate diagnosis with plasma and urine catecholamine measurements.7
- Plasma catecholamine levels, while simple to obtain, are of low diagnostic sensitivity and specificity compared to measurements from 24-hour urine collection.
- Plasma-free metanephrine levels after 30 minutes of supine rest are highly sensitive (99%), especially in those with genetic syndromes.
- Acidification is required to collect urine catecholamines but not metanephrine. A greater than 4-fold increase in urine metanephrine levels is highly sensitive for pheochromocytoma (97%).
- Urine vanillylmandelic acid has the highest specificity (95%).
- Abdominal ultrasound and other imaging with incidental findings of adrenal mass are becoming increasingly more common as the initial presentation.
- Abdominal computed tomography is considered the gold standard for diagnosis. Magnetic resonance imaging may be an alternative but provides lower spatial resolution.7 Additional nuclear imaging may be performed. Radiological studies are essential in determining location, extra-adrenal disease, functionality, metastasis, and surgical planning.
Perioperative Management
- The perioperative management and optimization of patients with suspected or confirmed pheochromocytoma require close collaboration with the surgeon, anesthesiologist, and endocrinologist. Optimizing a patient for pheochromocytoma surgery requires about 10-14 days of medical preparation. The main goals are controlling hypertension and tachycardia and restoring intravascular volume.1 The evaluation of end-organ dysfunction as a sequela of chronically elevated levels of plasma catecholamines should be investigated, with particular attention to the cardiovascular system.
- Alpha-blockers are the mainstay of preoperative treatment. They counter excess systemic catecholamine and improve intraoperative hemodynamic stability. Current guidelines recommend this practice despite no proven benefits in randomized trials. Nonselective alpha antagonists and selective alpha-2 antagonists have been used in this capacity.
- Phenoxybenzamine is a nonselective antagonist. It has a long half-life of approximately 24 hours.
- Doxazosin, terazosin, and prazosin are alpha-1 antagonists that have been used and are now favored due to their relatively shorter half-life.
- Alpha blockade should be gradually up-titrated for at least 7 days before surgery.
- A high sodium diet and fluid intake are used to facilitate volume expansion and limit orthostatic symptoms.1
- Selective and nonselective beta blockade is frequently used in patients with persistent arrhythmias or tachycardia, which is common in tumors that secrete large amounts of epinephrine and can be exacerbated with alpha blockade. Caution should be taken with beta blockade in patients with asthma and catecholamine-induced cardiomyopathy. Beta blockade should never be performed before alpha blockade due to the risk of further blood pressure elevations from unopposed alpha stimulation.
- Alternative medication choices include calcium channel blockers as well as inhibitors of catecholamine synthesis like metyrosine.3
Anesthetic Management
Preanesthetic Evaluation
- A comprehensive evaluation by the anesthesia provider should be performed, with special attention paid to the potential sequelae of chronic catecholamine excess and hypertension.
- Preoperative 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) should be used to detect signs of ischemia, arrhythmia, and hypertrophy.
- Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is necessary to assess the presence of catecholamine-induced cardiomyopathy. It may reveal hypertensive cardiomyopathy with a hypertrophic or dilated left ventricle with reduced function. TTE may also be used to monitor cardiac recovery following surgery.
- Assessing intravascular volume can be challenging. One should pay attention to clinical signs such as orthostatic hypotension or tachycardia. Elevated hematocrit is a laboratory finding that may suggest volume contraction.
- Those patients with secretory tumor type or high levels of free metanephrine are more likely to experience severe intraoperative hemodynamic swings. Prior to surgery, the adequacy of alpha-blockade and antihypertensive treatment should be assessed. The Roizen criteria is commonly used:3
- No in-hospital blood pressure of more than 160/90 mmHg for 24 hours before surgery
- No orthostatic hypotension with blood pressure less than 80/45 mmHg
- No ST or T wave changes for 1-week before surgery
- No more than five premature ventricular contractions per minute
Intraoperative Management
- Laparoscopy via a transperitoneal or retroperitoneal approach is considered the standard surgical approach for tumors under 15cm. Open approaches are often used for large tumors, paragangliomas with limited surgical access, and after failed laparoscopic approach. A robotic approach is a newer technique. Compared to the open approach, laparoscopy has been shown to provide excellent surgical visibility and exposure, be more hemodynamically stable, reduce catecholamine release, and improve postoperative recovery.3 There are critical portions of surgery that may precipitate episodes of intraoperative hemodynamic instability:
- Intubation can lead to exaggerated spikes in blood pressure and a deep plane of anesthesia should be achieved before airway instrumentation.
- Insufflation. Pneumoperitoneum often leads to a massive catecholamine surge with resultant hypertension and tachycardia. This response is likely a combination of mechanical compression and hypercarbia. This was the historical rationale behind the hesitancy to perform laparoscopy. However, deepening anesthesia, lowering the pressure of pneumoperitoneum, and increasing minute ventilation can reduce the risk of a hypertensive crisis.
- Tumor manipulation has been shown to cause the greatest release of catecholamines during the operative period.9 Meticulous surgical techniques to limit catecholamine release and close communication between the surgeon and anesthesiologist are key. Short-acting antihypertensive agents should be used in anticipation of adrenal venous clamping.
- The clamping of the adrenal vein associated with the tumor prevents catecholamine release and hypertensive crisis. However, hypotension is likely because of the sudden loss of catecholamine secretion. This effect is compounded by preoperative alpha blockade, intravascular volume depletion, and the intraoperative use of antihypertensive agents. This response is often exaggerated in patients with high levels of circulating catecholamines and patients with catecholamine-induced cardiomyopathy.10
- The anesthetic goals can be summarized as providing stable hemodynamics during excessive catecholamine surges and depletion during critical periods of surgery. The choice of medications used for anesthesia is less important than the adequate depth achieved to blunt the sympathetic activation.3
- Role of neuraxial anesthesia
- Spinal anesthesia should be avoided as profound hypotension may occur in patients who are hypovolemic from inadequate volume expansion.
- Epidural anesthesia should be considered for open procedures for postoperative pain management. Intraoperatively, sympatholysis from epidural anesthesia may not alleviate hypertension due to tumor manipulation. Additionally, hypotension after adrenal venous clamping and following tumor resection can be exacerbated by this sympatholysis.3
- Preoperative anxiolysis:
- Premedication with midazolam is recommended for most patients to help limit anxiety-driven catecholamine release before induction.
- Induction:
- Propofol is often used for induction. Etomidate may alternatively be used with the advantage of greater hemodynamic stability in hypovolemic patients.
- Intravenous or intratracheal lidocaine may be used for blunting sympathetic surges associated with laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation.
- Opioids such as fentanyl, remifentanil, and alfentanil, which do not induce histamine release, are recommended.
- Neuromuscular relaxation
- The nondepolarizing agents rocuronium and vecuronium are recommended.
- Maintenance
- Sevoflurane is the most widely used inhalational agent of choice. Isoflurane is a safe potential alternative.
- Total intravenous anesthesia is an acceptable maintenance strategy.3
- Postoperative nausea and vomiting
- Antiemetics with little or no dopaminergic blocking activity, such as ondansetron and fosaprepitant, may be used safely.
- Management of hypertension
- Short-acting vasodilators and beta-blockers should be readily available.
- Hypertension is treated by increasing the depth of anesthesia and administering direct-acting arteriolar vasodilators such as sodium nitroprusside, nicardipine, or cilnidipine. Adjunctive medications include nitroglycerine, esmolol, and phentolamine.
- Magnesium sulfate has the advantage of providing hemodynamic control via reducing catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla, decreasing catecholamine sensitivity, and providing arteriolar vasodilation. Magnesium has been shown to be useful in severe, resistant hypertension.2,10
- Dexmedetomidine infusions can additionally be used for the control of hypertension and tachycardia due to its alpha-2 effects.
- Management of Hypotension
- Short-acting vasopressors are the mainstay of treatment. Phenylephrine or norepinephrine, in combination with vasopressin or epinephrine, is commonly used.
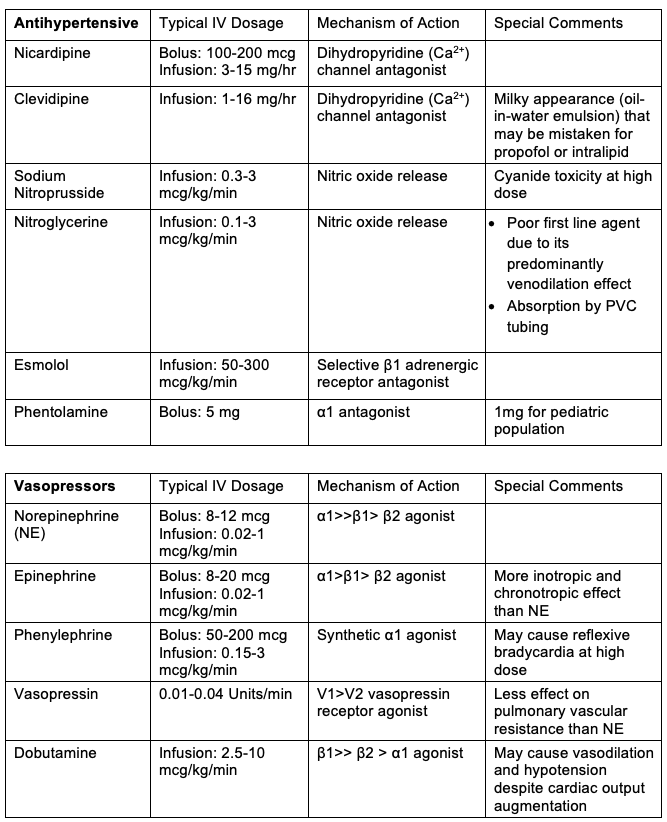
Table 1. Commonly used vasoactive medications, dosages, and mechanisms of action
- As a rule of thumb, medications with sympathomimetic properties, those that cause histamine release or have dopaminergic activity should be avoided.
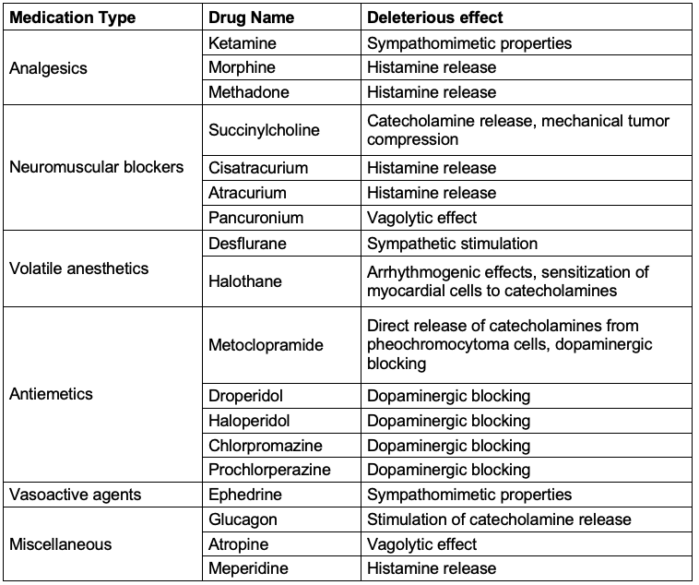
Table 2. Medications to avoid in patients with pheochromocytoma.2,3
Monitors and Access
- Standard American Society of Anesthesiologists monitors should be placed. Continuous ECG monitoring will alert the providers to any sign of myocardial ischemia or cardiac arrhythmia. Pulse oximetry will be valuable in detecting any pulmonary sequelae of cardiac dysfunction.
- In addition to noninvasive BP monitoring, invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring prior to induction is essential. This will allow close monitoring of the hemodynamic swings and easy access to blood sampling and laboratory tests.
- Adequate large-bore venous access is critical. The patient may be intravascularly depleted or may experience sudden hemorrhagic loss; both would require significant fluid resuscitation or transfusion.
- Central venous access is commonly obtained. In addition to being an easy avenue for volume replacement:
- It provides a reliable and effective way to deliver vasoactive infusions.
- Furthermore, central venous pressure — the filling pressure of the right heart — can be used as a surrogate for volume status.
- A central venous introducer sheath can be used to place a pulmonary artery catheter (PAC).
- If a history or signs of significant cardiomyopathy or coronary artery disease are present, transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) should be considered.
- TEE can monitor signs of ischemia (regional wall motion changes) during hemodynamic extremes or arrhythmia.
- It is a more reliable method to assess intracardiac preload and contractility.
- Alternatively, a PAC may be used if TEE is not feasible.
- It can provide pulmonary artery occlusive pressure, a surrogate for left heart filling pressure and preload.
- PAC can also be used to calculate cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance.
- However, the intraoperative PAC has largely fallen out of favor due to the lack of outcome benefits in trials and the unfamiliarity of many providers.
- Other considerations:
- Intraoperative glucose management should be closely monitored, given the hyperglycemic response to catecholamines and hypoglycemia after tumor resection.
- Bilateral adrenal tumor resection should necessitate a discussion between the surgeon, the endocrinologist, and the anesthesiologist regarding the need for glucocorticoid steroid replacement.
Postoperative Management
- Most patients can be monitored in the postoperative care unit and be admitted to the hospital wards for the first 24 hours after surgery.
- Up to half of the patients remain hypertensive after surgery, which is likely related to catecholamine stores in nerve endings.1 Prolonged hypotension is also common and may be related to residual alpha blockade or antihypertensive medications, blood loss, and altered vascular compliance.7
- The need for closer hemodynamic monitoring and the use of continuous intravenous vasoactive medications are indications for postoperative monitoring in the intensive care unit.
- Hypoglycemia should be anticipated in the immediate postoperative period due to loss of catecholamine suppression of insulin secretion. Hypoglycemia should be suspected in patients who are slow to wake up from anesthesia. Recent beta-blocker use can mask the clinical signs of hypoglycemia.3
- Adrenal insufficiency should be monitored in patients undergoing bilateral adrenalectomy.
References
- Wijeysundera D, Finlayson E. Preoperative Evaluation. In: Gropper et al. Miller’s Anesthesia. Volume 1. 9th Edition. Philadelphia, PA; Elsevier; 2020: 959-960, 1012.
- Ramakrishna H. Pheochromocytoma resection: Current concepts in anesthetic management. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2015;31(3):317-23. PubMed
- Naranjo J, Dodd S, Martin YN. Perioperative Management of Pheochromocytoma. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2017;31(4):1427-1439. PubMed
- Baez JC, Jagannathan JP, Krajewski K, et al. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: imaging characteristics. Cancer Imaging. 2012;12(1):153-62. PubMed
- O'Riordan JA. Pheochromocytomas and anesthesia. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 1997;35(4):99-127. PubMed
- La Batide-Alanore A, Chatellier G, Plouin PF. Diabetes as a marker of pheochromocytoma in hypertensive patients. J Hypertens. 2003;21(9):1703-7. PubMed
- Araujo-Castro M, Pascual-Corrales E, Nattero Chavez L, et al. Protocol for presurgical and anesthetic management of pheochromocytomas and sympathetic paragangliomas: a multidisciplinary approach. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021;44(12):2545-2555. PubMed
- Zuber SM, Kantorovich V, Pacak K. Hypertension in pheochromocytoma: characteristics and treatment. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2011;40(2):295-311. PubMed
- Joris JL, Hamoir EE, Hartstein GM, et al. Hemodynamic changes and catecholamine release during laparoscopic adrenalectomy for pheochromocytoma. Anesth Analg. 1999;88(1):16-21. PubMed
- Fernandez-Robles C, Carr ZJ, Oprea AD. Endocrine emergencies in anesthesia. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(3):326-334. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.