Copy link
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs
Last updated: 05/24/2023
Key Points
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are highly effective in treating both acute and chronic pain via inhibition of COX enzymes, reducing proinflammatory mediators of pain.
- All NSAIDs inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes with different selectivity. Ketorolac is more selective for COX-1 and thus is most likely to cause complications of gastrointestinal (GI) tract mucosa and promote bleeding. Celecoxib and meloxicam are more selective for COX-2 and, therefore, less likely to cause bleeding and GI tract effects.
- All NSAIDs must be used cautiously in patients with a history of thromboembolic disease, especially those with more COX-2 inhibition. Caution must also be exercised in patients with poor renal function, a history of peptic ulcer disease, or those on oral anticoagulants.
Mechanism of Action
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) exert their analgesic effect by preventing the formation of prostaglandins through the inhibition of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes.1 This prevents the downstream formation of other inflammatory mediators such as prostacyclin, prostaglandins E, F, D, and thromboxane A21-3(Figure 1).
- There are two subtypes of COX enzymes. COX-1 is constitutively expressed in various tissues, while COX-2 expression is induced only in tissues under stress. COX-1 production of prostaglandins and thromboxane is crucial for renal function, GI mucosal protection, hemostasis, and platelet aggregation.1,4 COX-2 expression is induced by tissue stress and inflammation and produces prostaglandins that increase pain and inflammation. 3,4
- While all NSAIDs inhibit both isoenzymes in varying ratios, drugs that more selectively target COX-2 are desirable since they affect the homeostatic functions of COX-1 to a lesser degree. Etodolac, meloxicam, and celecoxib are the most selective for COX-2 inhibition of the available NSAIDs.1,2,3
- Aspirin is notable for being an irreversible, nonselective inhibitor of the COX enzymes with long-lasting effects on platelet function, while other NSAIDs are competitive, reversible inhibitors.1
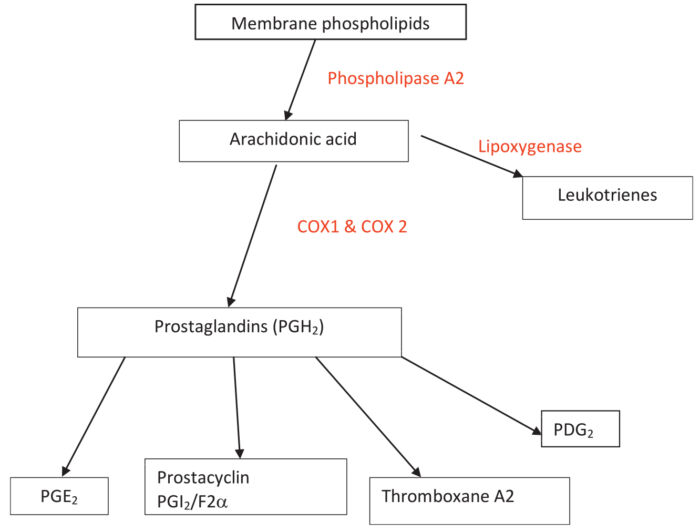
Figure 1. Arachidonic acid pathway showing production of prostaglandins from membrane phospholipids. Source: Sylvester J. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. WFSA Anesthesia Tutorial of the Week. CC BY NC ND 4.0. Link.
Pharmacokinetics
- NSAIDs are weak acids with pKa values of 5 or less, making them 99% ionized at pH values of 7 or above.1 They are highly protein bound with a low volume of distribution. Most NSAIDs are metabolized in the liver and excreted through biliary or renal pathways.3
Pharmacodynamics/Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal: COX-1 is required for the production of prostaglandins important for gastric mucosal protection.4
- Prostaglandin inhibition results in increased gastric acid secretion and the resultant propensity to form gastric/duodenal ulcers.3
- GI hemorrhage or perforation may result from both platelet inhibition and a lack of mucosal protection.3
- Ketorolac is an NSAID with the most selective COX 1 inhibition and thus is most prone to these side effects.3
- Cardiovascular: NSAIDs may increase the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in people who are at high risk for myocardial infarction (MI) or cerebrovascular accidents,2 and are used with caution in this population. They have also been shown to exacerbate hypertension.3
- Rofecoxib and other highly selective COX-2 inhibitors are no longer available due to a multifold increased risk of cardiac adverse effects (e.g., MI, heart failure).3
- Cardiovascular risks of nonselective NSAIDs are elevated compared to placebo.3
- Pulmonary: Patients with asthma are at an increased risk for leukotriene-mediated bronchoconstriction. This effect is most notable, historically, with aspirin use.2
- Renal: Prostaglandins produce renal vasodilation, affecting diuresis and natriuresis.4
- Patients with underlying renal dysfunction are at an increased risk for NSAID-induced kidney injury,4 particularly those who receive multiple NSAIDs concurrently or in combination with other nephrotoxic agents (gentamicin).2
- Interstitial nephritis is associated with NSAID use.2
- Hematologic: Platelet clotting function is closely related to COX-1 production of thromboxane. COX-2 is not expressed in platelets.3
- COX-2 inhibitors are not associated with increased perioperative bleeding.4
Clinical Uses
- Perioperatively, NSAIDs are most commonly used for analgesia. NSAID monotherapy is effective for the treatment of mild to moderate pain, and they are useful as multimodal analgesics with opioids for moderate to severe pain.4
- NSAIDs may be used as an antipyretic or in the treatment of gout, acute pericarditis, osteoarthritis, and in the management of many chronic pain conditions. They may even be used ensure the patency of the ductus arteriosus in certain congenital heart diseases.
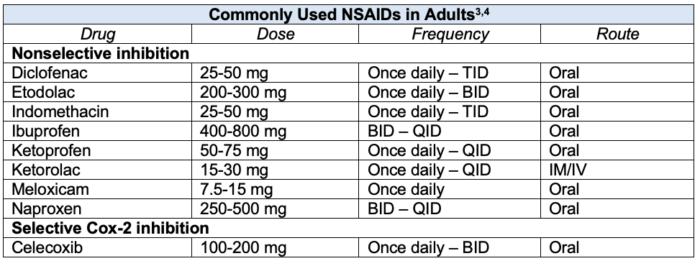
Table 1. Commonly used NSAIDs with adult doses
Special Considerations
- NSAIDs are highly protein bound.
- Other highly protein-bound drugs (e.g., oral anticoagulants, oral hypoglycemics, anticonvulsants) can be displaced by NSAIDs, increasing the free fraction of these medications, thereby potentiating their effect.1-3
- Patients with hypoalbuminemia (cancer, liver failure, malnourishment) may be more prone to toxicity from NSAIDs.3 Reduced dosing or avoidance of NSAIDs should be considered in this population.
- Nabumetone is metabolized to 6-methoxy-2-naphthyl acetic acid, an active metabolite more potent than its parent molecule.1 Patients with reduced kidney function are more likely to accumulate this metabolite, increasing the risk of toxicity.
- NSAIDs with half-lives greater than 12 hours are more associated with renal impairment. They should be used with caution in patients with reduced GFR.2,3
- These drugs include nabumetone, meloxicam, piroxicam, naproxen, celecoxib.
- Combining NSAIDs with angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitors or diuretics can lead to an increased risk of toxicity, including kidney injury and hyperkalemia.2
References
- Colvin L. Physiology and pharmacology of pain. In: Thompson, JP, Moppett IK, and Wiles M (eds). Smith and Aitkenhead’s Textbook of Anaesthesia. 7th ed. Edinburgh; Elsevier; 2019: 99-120.
- Aronson JK. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In: Aronson, JK. Meyler’s Side Effects of Drugs: the International Encyclopedia of Adverse Drug Reactions and Interactions. Sixteenth edition. Amsterdam, Netherlands; Elsevier; 2016: 236-72.
- Toda C, Naguib M. Peripherally acting analgesics. In: Flood P, Rathmell JP, and Urman RD (eds). Stoelting’s Pharmacology & Physiology in Anesthetic Practice. Sixth edition. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; Wolters Kluwer; 2022: 257-65.
- Hurley R, Elkassabany NM, Wu CL. Acute postoperative pain. In: Miller’s Anesthesia. 9th ed. Philadelphia; Elsevier; 2020:2620-22.
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.