Copy link
Crystalloids and Colloids
Last updated: 02/11/2025
Key Points
- Fluid management is a crucial part of perioperative anesthesia management. Crystalloids and colloids are two fluid categories that can be used for intravascular volume replacement. While both contribute to volume expansion, their mechanisms, applications, and potential complications differ.
- Choosing between crystalloids and colloids depends on several factors, including patient comorbidities, hemodynamic status, surgery type and needs, and availability.
- The current evidence suggests that balanced electrolyte crystalloids, such as lactated Ringer’s (LR) and Plasma-Lyte (PL), are generally preferred for routine intraoperative fluid management due to their safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness.1-4
- Colloids can have unwanted effects on the immune system, renal function, and coagulation. Colloids should be reserved for specific situations with clear indications and a careful assessment of the potential risks and benefits.3
Crystalloids
Crystalloids are aqueous solutions containing electrolytes and other solutes that resemble the body’s extracellular fluid. Their osmolarity, a measure of solute concentration, determines their tonicity, which influences how fluids move between intracellular and extracellular spaces.
Types of Crystalloids
- Hypotonic solutions: They have a lower osmolarity than extracellular fluid, leading to water movement into the cells, which can cause them to swell. Examples include 5% dextrose in water (which becomes hypotonic after metabolism) and 0.45% sodium chloride (½ NS). These solutions are primarily used in cases of hypernatremia or dehydration with intracellular fluid loss. Caution is needed to prevent cellular overhydration, which can lead to complications such as cerebral edema.
- Isotonic solutions: They have similar tonicity to extracellular fluid, maintaining osmotic balance. They are widely used intraoperatively for routine maintenance and volume expansion in conditions like dehydration and hypotension. Examples include LR, Hartmann’s solution (HS), normal saline (NS), and PL.
- Hypertonic solutions: They have a higher osmolarity than extracellular fluid, causing water to move out of the cells into the extracellular space, leading to cell shrinkage. Examples include 3% sodium chloride (hypertonic saline), 5% dextrose in 0.9% sodium chloride, and 10% dextrose in water. These solutions are used to treat conditions such as severe hyponatremia and cerebral edema by shifting fluid out of swollen cells. Caution is needed, as excessive use can lead to intravascular volume overload and potential complications such as pulmonary edema.
Deeper Dive into Isotonic Solutions
- LR and NS are the two most commonly used isotonic fluids. While both are effective in expanding intravascular volume, they differ in their electrolyte composition and metabolic effects (see Table 1).
- NS has a high chloride concentration and can contribute to hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, especially when used in large volumes. NS has also been linked to worsening hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis in renal failure patients, particularly during renal transplantation.4
- Balanced crystalloids (LR, PL, and HS) are intravenous (IV) fluids that contain electrolytes and buffers in concentrations designed to more closely resemble human plasma composition. Unlike NS, which contains only sodium and chloride, balanced crystalloids contain additional electrolytes (e.g., potassium, calcium, magnesium) and buffer solutions (e.g., lactate, acetate, gluconate) to reduce the risk of hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
- The SMART and SALT-ED trials suggested a potential benefit of balanced crystalloids in specific high-risk populations.5,6 In the SMART trial, balanced crystalloids were associated with a modest but significant reduction in kidney injury compared to NS in critically ill patients, whereas the SALT-ED trial showed similar results for hospitalized non critically ill patients. Both trials support the use of balanced crystalloids over NS in hospitalized patients, particularly those at risk for acute kidney injury (AKI).
- LR contains a balanced electrolyte profile, including lactate, which is metabolized to bicarbonate in the liver and kidney. This conversion helps buffer against metabolic acidosis, making LR a better choice for prolonged resuscitation.
- In patients with liver or renal failure, there is a theoretical risk that LR administration can lead to lactic acidosis due to impaired lactate metabolism.
- LR and HS are very similar, both containing lactate as a buffer, but HS has slightly more sodium and potassium.
- PL is the most balanced solution, closely resembling plasma with acetate and gluconate as buffers, plus magnesium.
- LR and HS contain calcium; therefore, they should not be mixed with blood products due to the risk of clot formation.
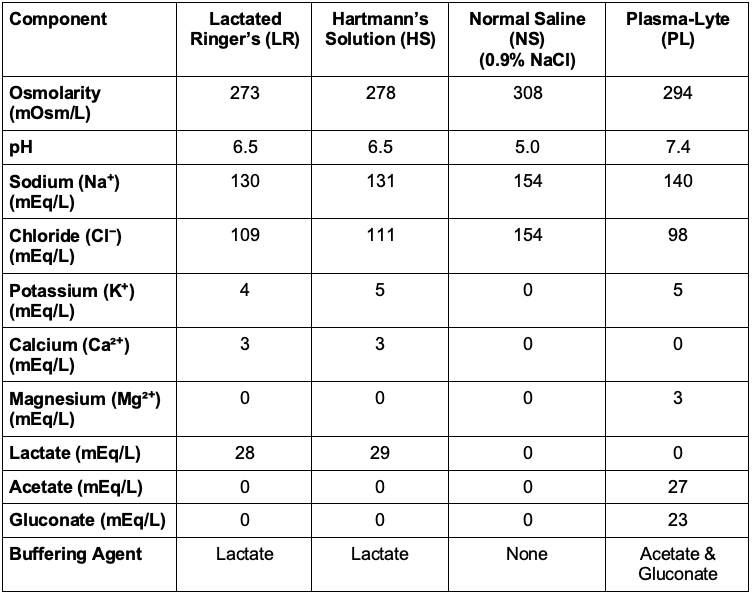
Table 1. Composition of isotonic solutions
Colloids
Colloids are IV solutions containing large-molecular weight substances, such as proteins or synthetic polymers, that do not readily cross cell membranes. They are primarily used to expand plasma volume and improve hemodynamic stability. Unlike crystalloids, colloids remain in the intravascular space for longer periods, theoretically making them more effective for resuscitation. However, their benefit is often limited in acute illness due to capillary leakage, which allows colloids to escape into the interstitial space, reducing their intravascular volume expansion effect.3
There are two main types of colloids:
Natural Colloids
- Human Albumin (5%, 25%): Derived from human plasma, albumin is a protein that effectively expands plasma volume and reduces interstitial edema. Despite its benefits, it is costly and can cause anaphylaxis. Moreover, the evidence does not consistently support superior hemodynamic outcomes compared to crystalloids.1,3,4
- Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP): FFP contains all coagulation factors, making it essential in managing coagulopathy. However, it is also expensive and carries a risk of anaphylaxis.1
Synthetic Colloids
- Hydroxyethyl Starch (HES): A synthetic polymer used to rapidly expand plasma volume, HES has a longer half-life than crystalloids. However, its use is associated with significant risks, including coagulopathy, renal dysfunction, and anaphylaxis. Studies in critically ill adult patients, particularly those with sepsis, have shown an increased mortality rate.7
- Dextran (low or high molecular weight): This synthetic polymer helps expand plasma volume and reduces blood viscosity. However, like HES, Dextran is associated with risks such as coagulopathy and renal dysfunction.
- Gelatins: Gelatins are less expensive than HES or Dextran but come with similar potential complications, including the highest rates of anaphylaxis. Their use is not approved in the United States.
Crystalloid versus Colloid Controversies
- While colloids remain useful in specific clinical contexts, such as managing coagulopathy or certain types of shock, the routine use of colloids in fluid resuscitation is increasingly questioned due to the limited evidence, associated risks, and higher costs.1-3, 7
- The CRISTAL trial suggests that while colloids have traditionally been used for resuscitation due to their ability to stay in the intravascular space, they may not offer superior benefits compared to crystalloids in critically ill patients. This has led to a reevaluation of routine colloid use in this patient population.3
- The debate over colloid use centers on three main points:
- Limited evidence: There is insufficient evidence to prove that colloids are more effective than crystalloids for routine fluid management.
- Potential risks: Colloids carry risks like anaphylaxis and kidney problems, which may outweigh their benefits.
- Cost: Colloids are more expensive than crystalloids, and their higher cost is difficult to justify, given their questionable benefits.
Complications and Side Effects
Crystalloids Complications
- Fluid overload: Excessive administration of crystalloids can lead to fluid overload, which may result in conditions like pulmonary edema, gastrointestinal wall edema, and worsened cardiac function.
Hemodilution: The infusion of large volumes of crystalloids can dilute blood components, potentially impairing oxygen delivery and clotting ability. - Acid-base disturbances and electrolyte disturbances: Large volumes of crystalloids can alter the body’s electrolyte balance, potentially leading to imbalances.
- NS: The high chloride content in NS can contribute to hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, especially when administered in large volumes. This condition can impair renal function and increase the risk of complications.8
- LR: It contains additional electrolytes, such as calcium and potassium, which can pose risks like hyperkalemia and hypercalcemia with excessive use.
- Lactate metabolism: Lactate in LR is metabolized in the liver (and to a lesser extent in the kidneys) into pyruvate, which is then converted into bicarbonate. This process helps to mitigate metabolic acidosis, unlike NS, which can induce acidosis during large-volume resuscitation.
- Considerations for liver and renal failure: LR should not be used in patients with end-stage liver disease, as their impaired metabolism of lactate can lead to lactic acidosis. In such cases, PL may be preferred.
- Blood transfusion consideration: LR should not be used as a diluting agent for blood transfusions because its calcium content can bind with the citrate anticoagulant in blood products, potentially leading to clotting issues.
Colloids Complications
- Anaphylaxis: There is a small risk of allergic reactions, which can be life-threatening.1,5
- Coagulopathy: Colloids can impair coagulation, increasing the risk of bleeding.1,5
- Renal dysfunction: Colloids can worsen renal function, particularly in patients with pre-existing renal conditions. For instance, in critically ill patients, the use of colloids has been associated with increased mortality and AKI, leading to recommendations against their use in such populations.1,5
- Cost-effectiveness: Colloids are generally more expensive than crystalloids, which raises concerns about their cost-effectiveness.1
- Cultural Considerations: Some colloids, like albumin, come from human donors. Certain patient populations, such as Jehovah’s Witnesses, may not accept these products due to religious beliefs.
- Hydroxyethyl Starches (HES): HES has negative effects on hemostasis and can cause renal toxicity.7 Hetastarch can impair platelet function, reduce plasma levels of Factor VII and von Willebrand factor, and weaken clot formation, leading to increased transfusion needs. The recommended dose is limited to 20mL/kg to minimize coagulopathy. Hetastarch can elevate serum amylase and is associated with anaphylactic reactions.
- Gelatin: Gelatin is not used in the U.S. due to rapid excretion in urine and a high incidence of anaphylaxis.
- Albumin: Albumin should be avoided in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. The SAFE trial showed higher mortality with albumin in trauma patients compared to NS.9
- Dextran: Dextran is associated with anaphylactic reactions, increased bleeding time, rare noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, and acute renal failure.
Fluid Redistribution: A Deeper Dive
Starling’s Forces: Fluid movement across capillary walls is governed by Starling’s forces, which include hydrostatic pressure, oncotic pressure, capillary permeability, and interstitial pressure.10 These forces determine the dynamic balance between fluid movement into and out of the intravascular space. Understanding fluid redistribution is crucial for accurately assessing a patient’s intravascular volume status.
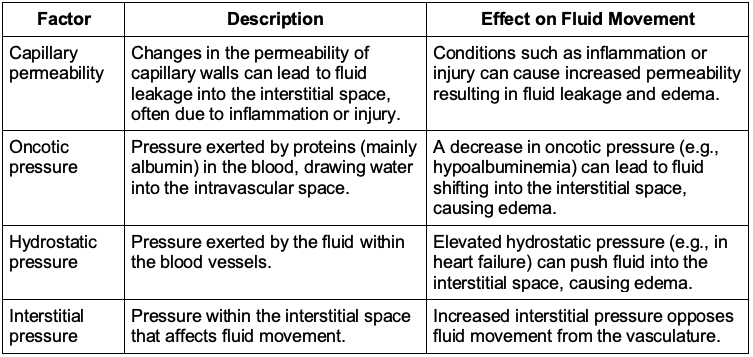
Table 2. Starling’s forces and their effects on fluid movement
Crystalloid Distribution and Redistribution
- Crystalloids distribute primarily in the extracellular fluid compartments, with a significant portion initially remaining in the intravascular space. However, over time, they tend to redistribute, with much of the fluid shifting into the interstitial space and less remaining in the intravascular compartment. This redistribution is influenced by Starling’s forces, which regulate fluid movement across capillary walls.10
- The phenomenon of “third spacing” refers to the accumulation of fluid in non-vascular spaces, such as the peritoneal or pleural cavities. This can occur due to alterations in Starling’s forces, such as fluid overload or a decrease in oncotic pressure, which can complicate fluid management further.11
Colloid Distribution and Redistribution
- Colloids are designed to remain within the intravascular space longer than crystalloids due to their larger molecular size. However, over time, colloids can redistribute into the interstitial space. This redistribution occurs because the large molecules can gradually leak through the capillary walls, especially in areas where the capillary permeability is increased due to inflammation or injury.12
- The extent and rate of colloid redistribution depend on several factors, including the molecular size of the colloid, the integrity of the capillary walls, and the presence of conditions that affect capillary permeability.
References
- Zazzeron L, Gattinoni L, Caironi P. Role of albumin, starches, and gelatins versus crystalloids in volume resuscitation of critically ill patients. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2016;22(5):428-36. PubMed
- Annane D, Siami S, Jaber S, et al. Effects of fluid resuscitation with colloids vs crystalloids on mortality in critically ill patients presenting with hypovolemic shock: the CRISTAL randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;310(17):1809-17. PubMed
- Lewis SR, Pritchard MW, Evans DJ, et al. Colloids versus crystalloids for fluid resuscitation in critically ill patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;8(8): CD000567. PubMed
- Saini V, Samra T, NaiK BN et al. Normal saline versus balanced crystalloids in renal transplant surgery: A double-blind randomized controlled study. Cureus. 2021;13(9):e18247. PubMed
- Self WH, Semler MW, Wanderer JP, et al. Balanced crystalloids versus saline in critically ill adults. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(9):829-839. PubMed
- Self WH, Semler MW, Bellomo R, et al. Balanced crystalloids versus saline in noncritically ill adults. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(9):819-28. PubMed
- Perner A, Haase N, Guttormsen AB, et al. Hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.42 versus Ringer’s acetate in severe sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:124-34. PubMed
- Kellum JA. Saline-induced hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Crit Care Med. 2002; 30:259-61. PubMed
- Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society Clinical Trials Group. A Comparison of Albumin and Saline for Fluid Resuscitation in the Intensive Care Unit. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350: 2247-56. PubMed
- Levick JR, Michel CC. Microvascular fluid exchange and the revised Starling principle. Cardiovasc Res. 2010; 87(2), 198–210. PubMed
- Hahn RG. Fluid escapes to the "third space" during anesthesia: a commentary. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2021; 65(1), 4–7. PubMed
- Holbeck S, Grände PO. Effects on capillary fluid permeability and fluid exchange of albumin, dextran, gelatin, and hydroxyethyl starch in cat skeletal muscle. Critical Care Medicine, 2000; 28(4), 1089–95. PubMed
Other References
- Bechtel A. Crystalloid resuscitation. OA Keys to the Cart. 2017 Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.