Copy link
Epidural Adjuvants: Clonidine and Dexmedetomidine
Last updated: 05/23/2023
Key Points
- Clonidine and dexmedetomidine are alpha2-adrenergic agonists that can potentiate analgesia when added to epidural solutions, with dexmedetomidine being more highly selective for alpha2-adrenergic receptors.
- Both clonidine and dexmedetomidine exert hemodynamic changes, mainly hypotension and bradycardia, that may impact a patient’s ability to tolerate the medications when administered via the epidural route.
- When combined with a local anesthetic in an epidural solution, both clonidine and dexmedetomidine will decrease the time of onset of the block and increase the duration of sensory blockade.
Mechanism of Action
- Clonidine and dexmedetomidine are alpha2-adrenergic agonists that produce analgesia via three mechanisms.1
- Stimulation of alpha2-adrenergic receptors in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, thus diminishing pain transmission (mimicking inhibitory descending bulbospinal neurons)
- Increased acetylcholine levels via the release of norepinephrine via the descending noradrenergic pathways, thus causing cholinergic activation in the dorsal horn
- Intrinsic blockade of Aδ and C fibers, thus its addition to local anesthetics, will potentiate sensor and motor blockade.
- Alpha2-adrenergic receptors are located on:
- primary afferent terminals (both at peripheral and spinal endings);
- neurons in the superficial laminae of the spinal cord; and
- within several brainstem nuclei implicated in analgesia.
- The presence of adrenoreceptors in these three sites supports the possibility of analgesic action at peripheral, spinal, and brainstem sites. However, clonidine is most potent in the neuraxial space.
- Clonidine is a centrally acting selective partial alpha2-adrenergic agonist, whereas dexmedetomidine is a highly selective alpha2-agonist.
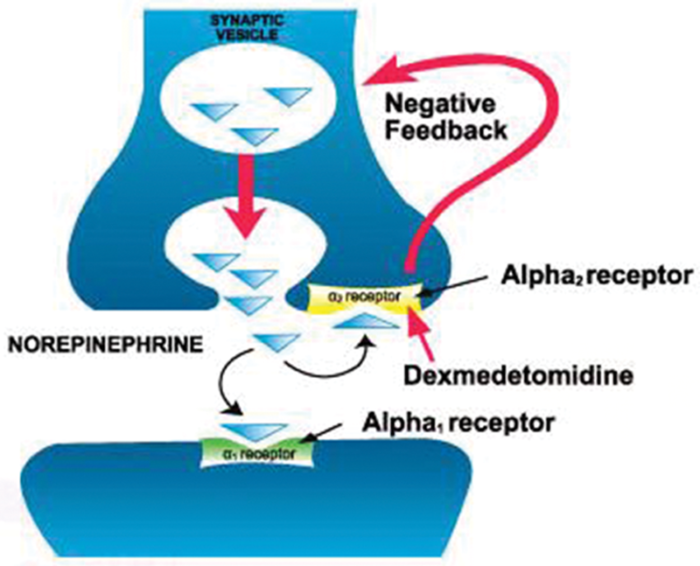
Figure 1. Dexmedetomidine is a potent and highly selective α-2 adrenoceptor agonist with sympatholytic, sedative, amnestic, and analgesic properties. The presynaptic sites of action are clinically significant because they modulate the release of norepinephrine and adenosine triphosphate through a negative feedback mechanism. Used with permission from Liu H, et al. Sedation after cardiac surgery: Is one drug better than another? Anesth Analg. 2017.2
Cardiovascular Effects
- Both clonidine and dexmedetomidine exert hemodynamic changes, mainly hypotension and bradycardia, that may impact a patient’s ability to tolerate the medications when administered via the epidural route.
- Dexmedetomidine administration can lead to varying degrees of heart block and thus should be used with caution in patients with hypovolemia, hypotension, bradycardia, fixed stroke volume, and advanced degrees of heart block.
- Most episodes of hypotension occur within the first 4 days of initiation of the epidural infusion.
- Given the cardiovascular impact of clonidine, the FDA has issued a black box warning for the use of epidural clonidine: “Clonidine hydrochloride injection (epidural clonidine) is not recommended for obstetrical, post-partum, or peri-operative pain management. The risk of hemodynamic instability, especially hypotension and bradycardia, from epidural clonidine may be unacceptable in these patients. However, in a rare obstetrical, post-partum or peri-operative patient, potential benefits may outweigh the possible risks.”3
- Due to concerns about hemodynamic changes in placental blood flow, clonidine is not routinely used in epidural solutions in the obstetrical population.
- Hemodynamic issues are dose-dependent, and studies have shown that in appropriate doses, effective analgesia can be delivered without unwanted cardiovascular effects.4
Clinical Use
The advantages of adding alpha2-adrenergic agonists to local anesthetic solution for epidural analgesia:5
- Decreased motor block without impacting analgesia as the local anesthetic dose can be reduced.
- When combined with a local anesthetic in an epidural solution, both clonidine and dexmedetomidine will decrease the time of onset of the block and increase the duration of sensory blockade (in comparison to local anesthetic alone).6
- They can eliminate the need for opioids in an epidural solution, thus removing the risk of opioid-related side effects such as respiratory depression, nausea, vomiting, and pruritis.
- They have a sedative effect in addition to analgesia, a side effect that may or may not be desired.
References
- Eisenach JC, De Kock M, Klimscha W. α2-Adrenergic agonists for regional anesthesia: a clinical review of clonidine (1984-1995). Anesthesiology.1996; 85(3): 655-74. PubMed
- Liu H, Ji F, Peng K, et al. Sedation after cardiac surgery: Is one drug better than another? Anesth Analg. 2017; 124(4):1061-70. PubMed
- Food and Drug Administration. Clonidine hydrochloride injection. FDA label search. Updated July 13, 2022. Accessed November 28, 2022. Link
- Huang YS, Lin LC, Huh BK, et al. Epidural clonidine for postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty: a dose–response study. Anesth Analg. 2007; 104(5):1230-5. PubMed
- Gabriel JS, Gordin V. Alpha 2 agonists in regional anesthesia and analgesia. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2001; 14 (6): 751-3. PubMed
- Gupta S, Raval D, Patel M, et al. Addition of epidural clonidine enhances postoperative analgesia: A double-blind study in total knee-replacement surgeries. Anesth Essays Res. 2010; 4(2): 70. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.