Copy link
Drug Shortages
Last updated: 11/21/2024
Key Points
- Drug shortages often result from imbalances between supply and demand.
- Drug shortages impact patient care, safety, and clinical outcomes.
- Addressing drug shortages requires coordinated efforts across healthcare systems. These efforts include early reporting, strategic management, and collaboration with regulatory bodies to ensure a reliable supply and minimize risks to patient care.
Introduction
- Drug shortages are a growing global issue, impacting nearly all areas of healthcare, including anesthesiology, where access to specific medications is essential for patient safety and effective care.
- Shortages of anesthesia drugs can result from various factors, such as manufacturing delays, quality control issues, supply chain disruptions, and increased demand. Together, these factors pose significant challenges to healthcare providers.
- Addressing drug shortages requires coordinated efforts across healthcare systems. These efforts include early reporting, strategic management, and collaboration with regulatory bodies to ensure a reliable supply and minimize risks to patient care.
Contributing Factors
- Drug shortages of sterile and injectable products can arise from several factors (Table 1).1
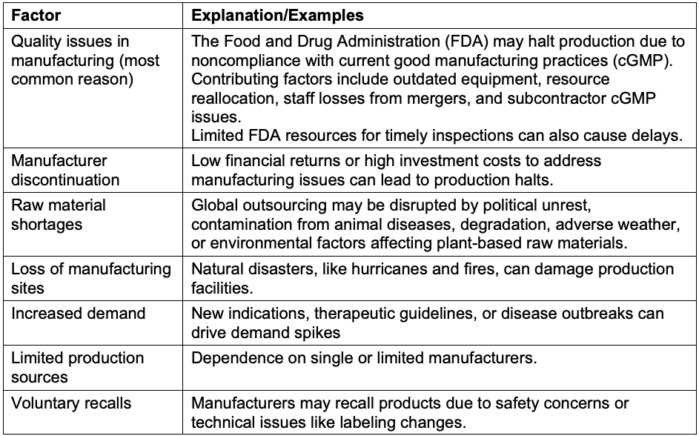
Table 1. Contributing factors to drug shortages1
Consequences
- Drug shortages significantly impact patient care and safety, resulting in:2
- Delayed or inadequate treatment leading to increased morbidity
- Higher costs to manage shortages
- Medication errors due to substitutions
- Unsafe or inappropriate substitution choices
- Improper use or handling of single-dose medications
- Multiple entries into single-dose vials which increase contamination risk and potential for infectious diseases such as hepatitis and human immunodeficiency virus
- Frustration, mistrust, and strained relationships between providers, manufacturers, pharmacies, prescribers, and patients
- Secondary shortages from sudden increased demand for alternative drugs
Strategies
- Some strategies to manage drug shortages are listed in Table 2.

Table 2. Strategies to manage drug shortages
Additionally, advocacy efforts for regulatory support and FDA involvement can be effective strategies.
- Push for governmental measures to:
- Increase drug inventories and production by private manufacturers
- Provide flexibility in regulations concerning manufacturing facilities
- Protect companies from liability risks
- Enhance profitability for generic drug manufacturers
- The FDA operates a program through its Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) to address drug shortages by collaborating with healthcare providers, organizations, and manufacturers.
- Depending on the cause of the shortage, the FDA can provide targeted assistance.
- Advocate for the FDA to implement Quality Reporting and Contingency Planning:
- A quality report card system for anesthesia-related drug suppliers
- Requirements for manufacturers to develop actionable contingency plans to reduce future shortage risks.
Stepwise Approach to Address Drug Shortages
- An organized approach to address drug shortages is shown in Figure 1.
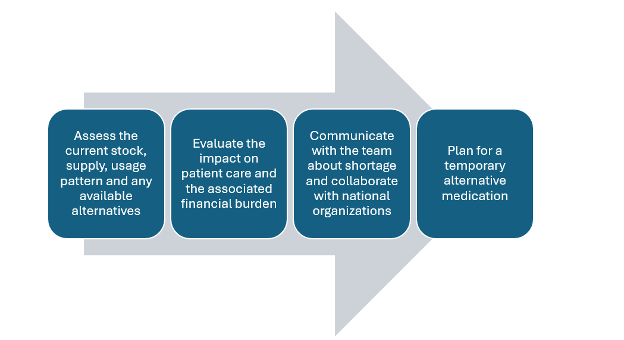
Figure 1. A stepwise approach to address drug shortages
Ethics
- Should patients be informed about drug shortages?
- Anesthesiologists face challenges in managing responsibilities for decisions related to drug shortages and in disclosing concerns to patients and colleagues. A formal shared decision-making approach may be an effective solution, as it would incorporate the perspectives of all stakeholders regarding shortages and their clinical implications.3
- Over 50% of patients who underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy at Mayo Clinic wanted to be informed of drug shortages that could impact their surgical care, even if the difference in potential side effects is as minor as the difference between acetaminophen and aspirin prescribed for headaches.4
Conclusion
- Anesthesia medication shortages can significantly impact patient care and safety, and anesthesiologists play a critical role in addressing these shortages by:
- Promptly notifying the ASA, FDA and ASHP of medication supply issues
- Implementing institutional guidelines to manage shortages
- Reporting cases in which medication shortage may have contributed to an adverse outcome to the Anesthesia Quality Institute
- Fostering collaboration between anesthesiology organizations and the FDA to help prevent future shortages
References
- Meyer T. The anatomy of drug shortages. Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation Newsletter. 2012; 27(1). Link
- De Oliveira GS Jr, Theilken LS, McCarthy RJ. Shortage of perioperative drugs: implications for anesthesia practice and patient safety. Anesth Analg. 2011;113(6):1429-35. PubMed
- Sinow C, Burgart A, Char DS. How anesthesiologists experience and negotiate ethical challenges from drug shortages. AJOB Empir Bioeth. 2021;12(2):84-91. PubMed
- Hsia IK, Dexter F, Logvinov I, Tankosic N, Ramakrishna H, Brull SJ. Survey of the national drug shortage effect on anesthesia and patient safety: a patient perspective. Anesth Analg. 2015;121(2):502-6. PubMed
Other References
- Warner, MA. Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation. 2019 President’s Report: Taking Action: APSF’s renewed commitment to the implementation of changes that can improve perioperative patient safety. Published February 2019. Accessed November 21, 2024. Link
- American Society of Health-Systems Pharmacists. Drug shortages as a matter of national security: Improving the resilience of the nation’s healthcare critical infrastructure. Published September 20, 2018. Accessed November 21, 2024. Link
- American Society of Health-Systems Pharmacists. Current drug shortages. Accessed November 21, 2024. Link
- American Society of Health-Systems Pharmacists. What you need to know about drug shortages. Published 2018. Accessed November 21, 2024. Link
- American Society of Health-Systems Pharmacists. How hospitals and health-systems manage drug shortages. Accessed November 21, 2024. Link
- Federal Drug Administration. Drug shortages. Updated October 3, 2024. Accessed November 21, 2024. Link
- American Society of Anesthesiologists. Drug and Equipment Shortages. Accessed November 21, 2024. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.