Copy link
Acute septic shock
Last updated: 05/30/2013
Septic shock is the final pathway of disseminated infection, and after respiratory failure, is the most common cause of admission to the ICU. The diagnosis of septic shock is based on identifying the probable source of infection, the systemic inflammatory response to infection and concomitant organ failure.
Patient with septic shock suffer an overwhelming systemic inflammatory response, with the final common pathway being multiple organ dysfunction and death.
Essential for successful treatment of sepsis is early recognition, rapid resuscitation, early administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics, identification of the source of the infection, and prompt treatment of infection.
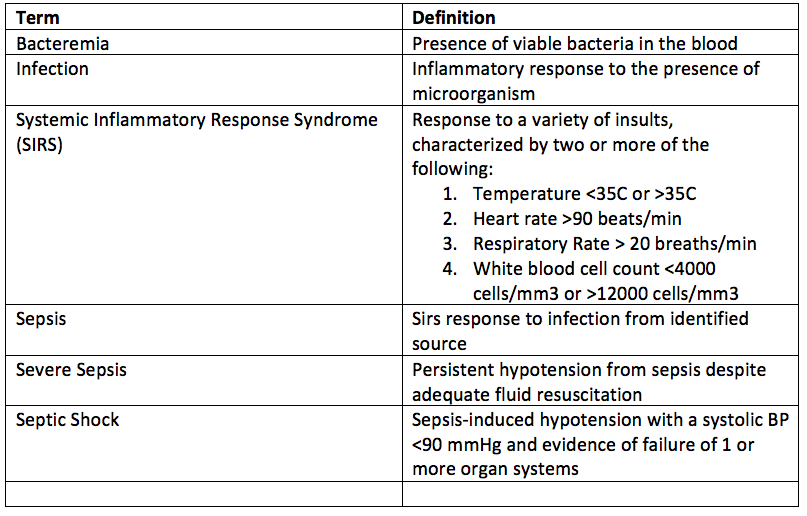
Table: Adapted from Miller, R.D (2005) Miller’s Anesthesia. New York: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone.
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.