Copy link
Acetazolamide
Last updated: 07/30/2025
Key Points
- Acetazolamide is a reversible carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that exerts its impact systemically by reducing bicarbonate resorption.
- It is used in the treatment of edema, glaucoma, some conditions associated with a predisposition to intracranial hypertension, seizures, some forms of metabolic alkalosis, and altitude sickness.
- Caution should be used in patients with sulfa allergies, renal failure, or electrolyte abnormalities.
Introduction and Mechanism of Action1
- Carbonic anhydrase (CA) is a zinc-containing metalloenzyme that catalyzes the reversible reaction shown below.
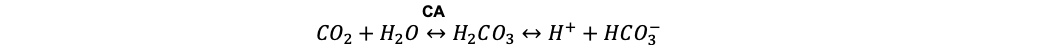
- This reaction is crucial for maintaining acid-base balance, facilitating carbon dioxide transport, and regulating electrolyte balance. Thus, any agent capable of inhibiting this enzyme will shift the equilibrium towards the formation of carbon dioxide and water, reducing bicarbonate formation and promoting metabolic acidosis.
- Acetazolamide was developed for use as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and became the first sulfonamide-derived carbonic anhydrase inhibitor approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1954. Its initial use was primarily as a diuretic due to its ability to promote bicarbonate and sodium excretion in the urine. However, because of the risk of metabolic acidosis, it fell out of favor when more effective diuretics (i.e., loop diuretics) were subsequently developed.
- While it is still used in the management of alkalosis, acetazolamide has now found greater utility in the treatment of medical conditions such as glaucoma, intracranial hypertension, and acute altitude sickness, among others.
Key Locations of Carbonic Anhydrase
- While CA is found in various tissues throughout the body, including the red blood cells, acetazolamide has found particular use in exhibiting its effects on the enzyme in the following locations.
- Kidneys: CA is located in the proximal tubule of the nephron. Under normal circumstances, bicarbonate is resorbed within the proximal tubule leading to promotion of Na+/H+ ion exchange, indirectly aiding sodium, chloride, and water reabsorption while promoting H+ excretion. Acetazolamide administration results in the loss of bicarbonate, sodium, chloride, and potassium in the urine, with subsequent hydrogen ion retention leading to hypokalemic metabolic acidosis and diuresis. Laboratory findings in a patient on chronic acetazolamide therapy include metabolic acidosis from bicarbonate loss and decreased hydrogen ion secretion. There also might be hyponatremia and hypokalemia.
- Eyes: The ciliary body is responsible for the production of aqueous humor, which requires bicarbonate for ion transport and creation of an osmotic gradient. Administration of acetazolamide inhibits the production of bicarbonate, decreasing aqueous humor production and, therefore, intraocular pressure.
- Brain: CA is requisite at the level of the choroid plexus to produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Like the kidney, the epithelium of the choroid plexus uses an osmotic gradient to drive water into the ventricles. Acetazolamide use disrupts this osmotic gradient, resulting in decreased CSF production, making the drug useful in lowering intracranial pressure. Additionally, CA mediates neuronal excitability by altering the CO2-H+-HCO3– equilibrium. By inhibiting HCO3– efflux, acetazolamide may prevent abnormal gamma-aminobutyric acid-A-mediated depolarization that contributes to epileptic discharges, thereby making the drug useful in the treatment of epilepsy.
- Lungs: Within red blood cells (RBCs), acetazolamide prevents the conversion of bicarbonate to carbon dioxide, leading to an accumulation of hydrogen ions in RBCs and throughout the body. The acidosis then stimulates the respiratory center of the brain, leading to increased ventilation, making the drug useful as an adjunct in the treatment of central sleep apnea. Similarly, in altitude sickness, a person has ascended too quickly, resulting in symptoms commonly associated with hypobaric hypoxia. The use of acetazolamide then leads to increased ventilation, improved oxygenation, and faster acclimatization.
Indications and Dosing2-4
Acetazolamide and Acetazolamide Sodium
- Acetazolamide is available in oral and injectable forms. The injectable form includes sodium to prevent nonsensical wasting in the kidneys and hyponatremia. Acetazolamide is not approved by the United States FDA for use in the pediatric population. However, there are several off-label uses of this medication.
Glaucoma
Acute angle-closure glaucoma
- 500mg intravenous (IV) or per oral (PO) loading dose, once, followed by 125-250mg PO/IV every 4 hours; doses exceeding 1g/day are rarely more effective.
Open-angle glaucoma
- 125 – 250mg PO/IV twice daily to four times daily, or 500mg extended-release PO twice daily; doses exceeding 1g/day are rarely more effective.
Secondary glaucoma
- 250mg PO/IV q4h, or 500mg extended-release PO twice daily; doses exceeding 1g/day are rarely more effective.
Altitude Sickness
Prevention, when knowingly ascending higher than 2000m
- 125mg PO twice daily, until descent or upon arrival at stable altitude for 2 – 4 days
Acute mountain sickness
- 250mg PO twice daily until descent or 24 hours after symptoms resolve
- Best used as an adjunct to dexamethasone
High-altitude cerebral edema (adjunct only)
- 250mg PO twice daily until descent or 24 hours after symptoms resolve
Edema (Secondary to heart failure, generalized edema, and drug-induced edema)
- 250 – 500mg PO/IV once daily or every other day, until euvolemia is restored
- Used as an adjunct to other diuretics, such as furosemide
Epilepsy (unlocalized seizures, adjuvant therapy)
- 375 – 1000 mg PO, divided into two or four times daily
- Dosing initiated at 250mg and uptitrated as an adjunct to other anticonvulsants
Off-Label Use
Central sleep apnea
- 125 – 500 mg PO daily, doses exceeding 500mg/day are rarely more effective
Metabolic alkalosis reversal
- 500mg IV/PO once, can repeat as needed based on acid-base status
- Additional dosing with a maximum of 250 – 500 mg twice daily
- IV is the preferred route of administration for this indication.
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- 250 – 500 mg PO twice daily, titrated to a maximum of 4g daily
Contraindications2-4
Hypersensitivity
- Hypersensitivity to acetazolamide or other ingredients in the formulations. This also encompasses hypersensitivity to sulfonamides, since acetazolamide is a sulfonamide derivative.
Hepatic Disease
- This includes hepatic insufficiency due to genetic, infectious, autoimmune, drugs, toxins, and vascular etiologies. It is contraindicated in any patient with cirrhosis as it increases the risk of hepatic encephalopathy.
Baseline Electrolyte Derangements
- Specifically, patients who have hyponatremia or hypokalemia prior to initiation of acetazolamide
- It is also contraindicated in patients with adrenal insufficiency and hyperchloremic acidosis, due to the concern of exacerbating existing electrolyte imbalances.
Severe Renal Disease
- Acetazolamide is almost exclusively cleared by the kidneys, and marked kidney impairment can lead to toxic accumulation of the drug. Furthermore, because it is a diuretic, acetazolamide can worsen kidney function. If the benefits of acetazolamide use outweigh the risks of worsening kidney function, there are adjusted dosing guidelines based on a patient’s creatinine clearance and glomerular filtration rate.
- In dialysis-dependent patients, the use of acetazolamide is not recommended, as it is only 30% cleared by hemodialysis and almost 0% by peritoneal dialysis. This can lead to severe CNS toxicity.
Chronic Noncongestive Closure Glaucoma
- Long-term use of acetazolamide is contraindicated as it may lead to organic closure of the drainage angle. This can worsen a patient’s glaucoma while it is masked by low intraocular pressure
Contraindications2-4
Aplastic Anemia
- Occurs within 7 weeks – 3 months of initiation, and it is not dose-related.
Growth Retardation
- Noted in children with chronic use more than 1 year
- Growth rates have been shown to return to normal after cessation of the drug.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Immediate reactions are noted in patients who have known hypersensitivities to sulfonamide drugs. This includes anaphylaxis and urticaria.
- Delayed hypersensitivity reactions are also noted, ranging from a maculopapular rash to more severe cutaneous reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome. This is attributed to acetazolamide being a sulfonamide derivative.
Severe Metabolic Acidosis
- Typically, in diabetic patients, older adults, patients with kidney impairment, and patients with uncompensated or severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Toxicity1,5
- Patients with kidney impairment are at the highest risk of acetazolamide toxicity, leading to a metabolic encephalopathy and even coma in some cases. Symptoms may initially present as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, abdominal pain, increased urination, and confusion. Hyperammonemia may also occur, presenting with neurologic deficits such as asterixis.
- Treatment of acetazolamide toxicity is immediate cessation of the drug, followed by supportive care to correct the metabolic acidosis and electrolyte imbalances. If overdose is suspected, a gastric lavage may also be performed to decrease absorption of acetazolamide into the system.
- Additionally, acetazolamide is a CYP3A4 inhibitor. This raises concerns for patients who take metformin, high-dose aspirin, and certain anticonvulsants, as it can prevent the metabolism of these drugs, leading to secondary accumulation. Toxic levels of any CYP-dependent medications may lead to severe metabolic acidosis, including lactic acidosis.
References
- Farzam K, Abdullah M. Acetazolamide. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2025. Accessed June 10, 2025. Link
- Acetazolamide: Drug Information. UpToDate. Accessed June 10, 2025. Link
- Endo Operations. Acetazolamide Sodium [package insert]. US Food and Drug Administration. Published June 20, 2017. Accessed June 10, 2025. Link
- Teva Pharmaceuticals. Diamox [package insert]. US Food and Drug Administration. Published September 20, 2024. Accessed June 10, 2025. Link
- Chak G, Patel R, Allingham R. Acetazolamide: considerations for systemic administration. EyeNet Magazine. Published March 1, 2015. Accessed June 10, 2025. Link
Other References
- Bechtel A. OpenAnesthesia. Keys to the Cart. Acetazolamide, Mountain Sickness. Created June 26, 2017. Accessed July 30, 2025. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.