Copy link
Abnormal ECG: Catecholamines
Last updated: 12/21/2015
Catecholamine surges are thought to be pathogenic in stress (takotsubo) cardiomyopathy (1). This catecholamine induced injury causes ventricular ballooning, dysfunction, and in some cases dysrhythmia and sudden death. The diagnosis is confirmed with echocardiography or cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Coronary angiography may be necessary to rule out ischemic cardiomyopathy in some cases.
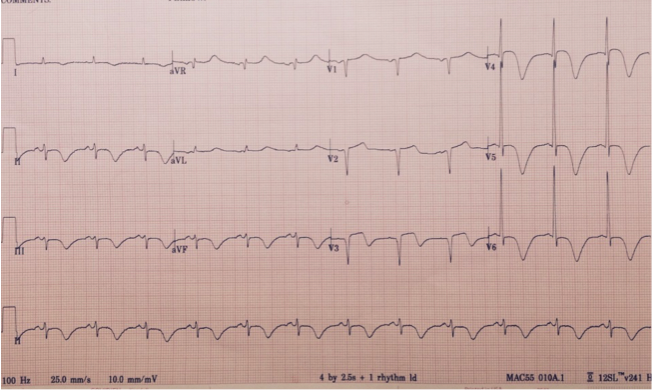
Troponin levels are typically mildly elevated in stress cardiomyopathy and the most common EKG findings are ST elevation and T-wave inversion (1). In the setting of massive stroke or intracerebral hemorrhage, the classic EKG has deep, diffuse T-wave inversions (see figure). The etiology in this setting is also thought due to catecholamine surges. More common are subtler T-wave inversions, ST changes, and/or dysrhythmias.
Other References
- Cardiac Complications of Stroke Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.