Copy link
Prolonged QT Intervals and Cardiac Channelopathies
Last updated: 01/24/2025
Key Points
- A prolonged QT interval increases the risk of causing torsades de pointes, a life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia.
- Cardiac channelopathies involve multiple different ion channels from various genes and can have a wide range of clinical implications and resulting conditions.
- Patients with prolonged QT and inherited cardiac channelopathies are at high risk for perioperative arrhythmias.
- Anesthetic management should focus on close hemodynamic monitoring, adequate anesthesia and analgesia, and maintenance of normocarbia, normothermia, and normovolemia.
Overview and Pathophysiology
QT Interval
- The QT interval can be described as the time from the beginning of ventricular depolarization (Q wave on electrocardiogram [ECG]) to the end of ventricular repolarization (T wave on ECG).1
- The QT interval can vary depending on various factors, including age, sex, and heart rate. Bradycardia prolongs the QT interval, while tachycardia shortens the QT interval.1
- There are several formulas to correct for a QT (noted as QTc)1:
- Bazett: QT/RR1
- Fridericia: QT/RR1,2
- Framingham: QT + 0.154(1-RR)
- Hodges and Colleagues: QT – 1.75(HR-60)
- The parameters of a normal, borderline, and prolonged QTc are listed in Table 1.
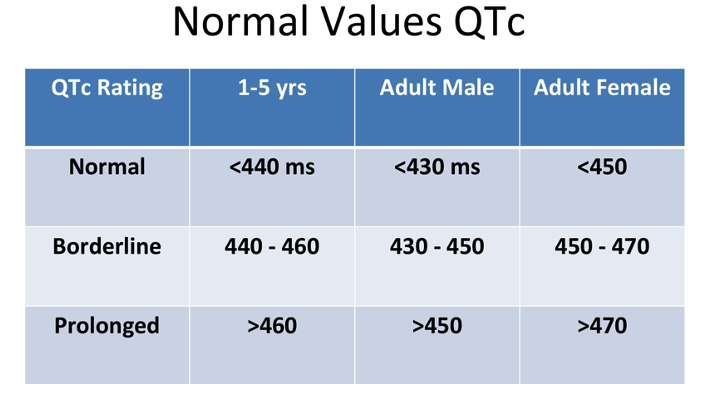
Table 1. Normal, borderline, and prolonged corrected QT interval. Adapted from Schulein S. Long QT SAJAA. 2010;16(3): 84-87. Link
Causes of Prolonged QT Interval2
- Medical causes: myocardial ischemia, sinus node dysfunction, hypothyroidism, hypothermia, cocaine abuse, human immunodeficiency virus infection, intracranial diseases, etc.
- Electrolyte abnormalities: hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia
- Drugs:
- Antipsychotics: haloperidol, ziprasidone, quetiapine, thioridazine, olanzapine, risperidone
- Antiarrhythmics: amiodarone, sotalol, dofetilide, procainamide, quinidine, flecainide
- Antibiotics: macrolides, fluoroquinolones
- Antidepressants: amitriptyline, imipramine, citalopram, amitriptyline
- Antiemetics: droperidol, 5-HT3 antagonists (ondansetron, dolasetron, granisetron), metoclopramide
- Inhaled anesthetics: sevoflurane
- Diuretics: furosemide, hydrochlorthiazide
- Others: methadone, sumatriptan, cisapride3
Torsades de Pointes
- A prolonged QT can increase the risk of torsades de pointes, a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia noted for its twisting QRS complexes of varying magnitude on ECG. Torsades can be life-threatening and can lead to complications such as syncope, seizures, or even sudden cardiac death if not managed appropriately.3
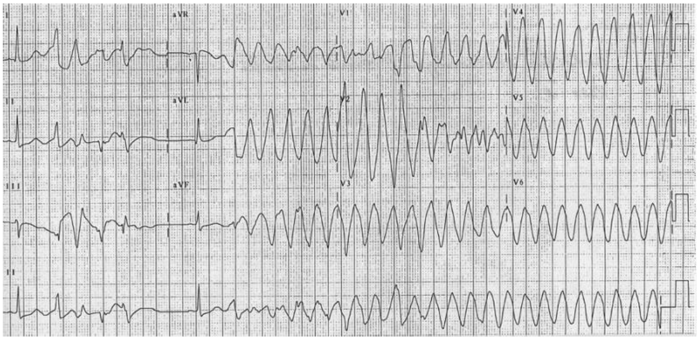
Figure 2. 12-lead electrocardiogram of torsades de pointes. Source: CardioNetworks via Wikimedia Commons. 2010. Link
- Management of Torsades de Pointes2
- Prevent initial onset by avoiding QT prolonging drugs if possible and correcting electrolyte abnormalities.
- When torsades occurs, most episodes are self-limiting. However, there is a risk of the patient developing ventricular fibrillation.
- Magnesium (slow 2 g IV push with an infusion of 1 gm to 4 gm / hour until serum levels greater than 2 mmol/L) should be administered as soon as possible to stabilize the cardiac membrane.
- Synchronized electrical cardioversion should be performed on patients who are hemodynamically unstable.
- Pulseless patients should be defibrillated.
- Another option for torsades is overdrive pacing to increase the heart rate.
Cardiac Channelopathies
Channelopathies
- Cardiac channelopathies are a group of genetic or acquired disorders that involve the dysfunction of myocardial ion channels such as potassium, sodium, and calcium.3
- These channelopathies lead to altered permeabilities of ion channels, which lead to3:
- Proarrhythmic ECG changes and sudden unexplained cardiac death.
- Delayed ventricular repolarization.
- Prolonged QT → torsades de pointes
- Heterogenous depolarization
- Cardiac channelopathies can be subcategorized into the following:
- Congenital long QT syndrome (c-LQTS)
- Brugada syndrome
- Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
- Sick sinus syndrome (SSS)
- Short QT syndrome (SQTS)
- Cardiac conduction disease (CCD)
- Familial atrial fibrillation
Congenital Long QT Syndrome
- Long QT syndrome is an inherited (c-LQTS) or acquired disorder of cardiac ion channels that impacts cellular repolarization and results in tachyarrhythmias due to a prolonged QT interval.3
- Multiple genes, loci, proteins, and ion channels can be at fault for congenital long QT, with the most commonly affecting genes being KCNQ1, KCNH2, and SCN5A.4
- The major c-LQTSs are Romano Ward syndrome (autosomal dominant with normal hearing) and Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (autosomal recessive with associated sensorineural hearing loss).4
- The administration of IV magnesium sulfate infusion is key to preventing the occurrence of torsades de pointes in patients with c-LQTS.4
Brugada Syndrome
- Brugada syndrome is an inherited disorder (usually in the SCN5A gene) characterized by right ventricular conduction delay and right-sided ST changes.5
- Identified by ST segment elevations in leads V1-V3 and a pseudo right bundle branch block (Figure 3).5
- Brugada syndrome predisposes to ventricular arrhythmias, predominantly ventricular fibrillation, as opposed to torsades de pointes from c-LQTS.5
- The ECG changes of Brugada can be reversed with the administration of isoproterenol.3
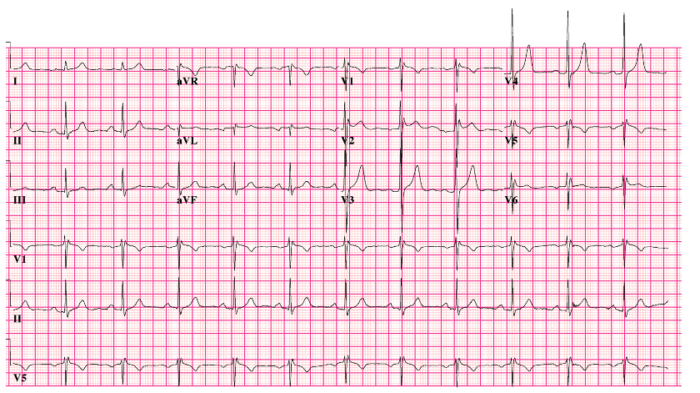
Figure 3. 12-lead electrocardiogram of Brugada syndrome. Source: CardioNetworks via Wikimedia Commons. 2010. Link
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- A rare hereditary disease characterized by adrenergic-dependent arrhythmias that can be lethal.
- Often, there is a family history of syncope or sudden death in 30% of affected patients.6
- Often diagnosed by ECG changes during exercise.
- Therapy consists of β-blockers and the placement of an implantable cardiac defibrillator.
Sick Sinus Syndrome
- A collection of disorders due to sinus node dysfunction and the inability of the heart to perform adequate pace-making and sinus rhythm. SSS can be due to a channelopathy, degenerative fibrosis, or secondary to medications or metabolic abnormalities.7
- Commonly seen in older patients, SSS can present as bradycardia, with some patients experiencing an accompanying tachycardia (known as tachy-brady syndrome).7
- As the disease progresses, symptoms begin to become more notable due to cerebral and other end-organ hypoperfusion.7
- Although not curable, the insertion of a pacemaker can help to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.7
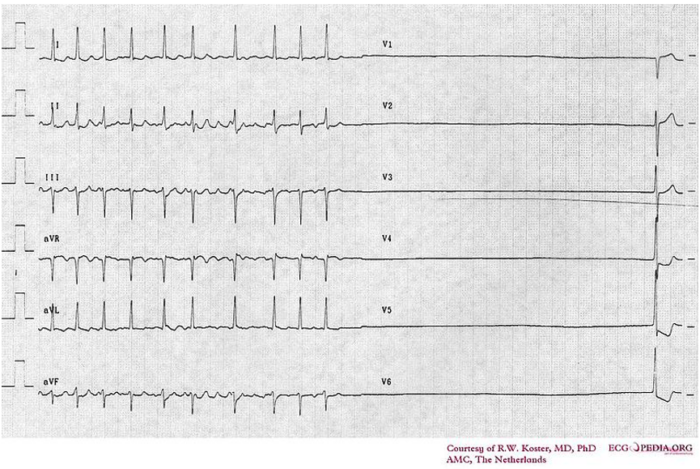
Figure 4. Electrocardiogram of sick sinus syndrome. Source: Cardionetworks via Wikimedia Commons. 2007. Link
Short QT Syndrome
- Similarly to long QT syndrome, SQTS is a rare inheritable channelopathy.8
- SQTS is comprises accelerated cardiac repolarization that leads to the development of life-threatening arrhythmias.8
- Patients with SQTS may experience cardiac arrest from the early neonatal period or not until the age of 80.8
- The main genes affected are KCNH2, KCNQ1, KCNJ2, CACNA1C, and CACNB2, which impact the transcription of L-type calcium or potassium channels.8
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators or quinidine can be used to manage arrhythmias and prolong QT interval.8
Cardiac Conduction Disease
- A group of diseases that impact the heart’s electrical conduction system including the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers, or bundle branches.9
- CCD can lead to heart block, conduction block, or other cardiac delays, manifesting as bradycardia, syncope, and sudden cardiac death.9
- In addition to inherited causes (such as the SCN5A gene), CCD can be caused by degenerative conditions, ischemia, infiltrative diseases, or inflammatory conditions.9
- Treatment includes pacemaker implantation for patients with symptomatic bradycardia or high-degree heart block.9
Familial Atrial Fibrillation
- An inherited form of atrial fibrillation that has similar uncoordinated electrical activity in the atria leads to a rapid irregularly irregular heartbeat that leads to indiscernible p-waves on ECG. This can lead to embolus formation in the atrial appendage and result in stroke/sudden death.10
- Familial atrial fibrillation is an autosomal dominant condition that involves the SCN5A, KCNQ1, KCNJ2, KCNH2, and MYL4 genes.10
- While diagnostic ECG and physical findings are like nonfamilial atrial fibrillation, the combination of family history, clinical evaluation, and genetic testing can help identify familial atrial fibrillation.10
- Management is the same as general atrial fibrillation, with rate/rhythm control in combination with possible anticoagulation.10
Anesthetic Considerations in Patients with Cardiac Channelopathies
- Patients with inherited cardiac channel disorders are at high risk for perioperative arrhythmias.3
- Anesthetic management includes preoperative anxiolysis, maintaining stable hemodynamics, providing adequate anesthesia and analgesia, and maintaining normocarbia, normothermia, and normovolemia.3
- In c-LQTS, a magnesium sulfate bolus (30 mg/kg iv) and infusion should be administered to prevent torsades de pointes.3
- Drugs such as droperidol, ketamine, succinylcholine, and ondansetron should be avoided.3
β-blocker therapy should be maintained. Propofol is a suitable anesthetic agent; fentanyl and dexmedetomidine are good choices, and inhalational agents should be used cautiously.3 - In Brugada syndrome, avoid β-blockers, α-blockers, and cholinergic drugs. Isoproterenol should be available for any ECG changes.3 Propofol and volatile anesthetics have been safely used.
- In catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, β-blockers should be continued and β-agonists should be avoided, such as isoproterenol. Remifentanil is a good analgesic. Intraoperative tachycardia should be treated with a β-blocker such as esmolol or labetalol. Postoperative nausea and vomiting should be avoided; the stress can invoke arrhythmias.3
References
- Castiglione A, Odening K. QT-Zeit – Was fange ich eigentlich damit an? [QT Interval and Its Prolongation - What Does It Mean?]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2020;145(8):536-542. PubMed
- Gowda RM, Khan IA, Wilbur SL, Vasavada BC, Sacchi TJ. Torsade de pointes: the clinical considerations. Int J Cardiol. 2004;96(1):1-6. PubMed
- Staikou C, Chondrogiannis K, Mani A. Perioperative management of hereditary arrhythmogenic syndromes. Br J Anaesth. 2012;108(5):730-744. PubMed
- Webster G, Berul CI. An update on channelopathies: from mechanisms to management. Circulation. 2013;127(1):126-140. PubMed
- Gussak I, Antzelevitch C, Bjerregaard P, Towbin JA, Chaitman BR. The Brugada syndrome: clinical, electrophysiologic and genetic aspects. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999;33(1):5-15. PubMed
- Ylänen, K., Poutanen, T., Hiippala, A. et al. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Eur J Pediatr 169, 535–542 (2010). Link
- Semelka M, Gera J, Usman S. Sick sinus syndrome: a review. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87(10):691-696. PubMed
- Mazzanti A, Underwood K, Nevelev D, Kofman S, Priori SG. The new kids on the block of arrhythmogenic disorders: Short QT syndrome and early repolarization. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017;28(10):1226-1236. PubMed
- Li T, Marashly Q, Kim JA, et al.: Cardiac conduction diseases: understanding the molecular mechanisms to uncover targets for future treatments. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2024;28:385-400. Link
- Jurkko R, Palojoki E, Huttunen H, et al. Characteristics of atrial fibrillation and comorbidities in familial atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013;24(7):768-774. PubMed
Other References
- QT Drugs List on Crediblemeds.org (Requires free registration). Accessed: January 22, 2025. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.